YouTube Content Filtering and Management: A Professional Guide for 2025
Executive Summary
YouTube processes over one billion hours of video consumption daily, making effective content management essential for individuals, families, and organizations. This comprehensive guide examines current methods for filtering and controlling YouTube content across personal, parental, and institutional contexts while maintaining compliance with platform policies and legal frameworks.
Understanding YouTube’s content management ecosystem requires recognizing a fundamental distinction: the platform does not offer universal channel blocking for standard accounts. Instead, content control operates through algorithmic influence, specialized parental tools, and institutional network management. This guide provides actionable frameworks for implementing appropriate content governance strategies based on organizational or personal requirements.
Part I: Algorithmic Content Management for Standard Accounts
Understanding YouTube’s Recommendation Architecture
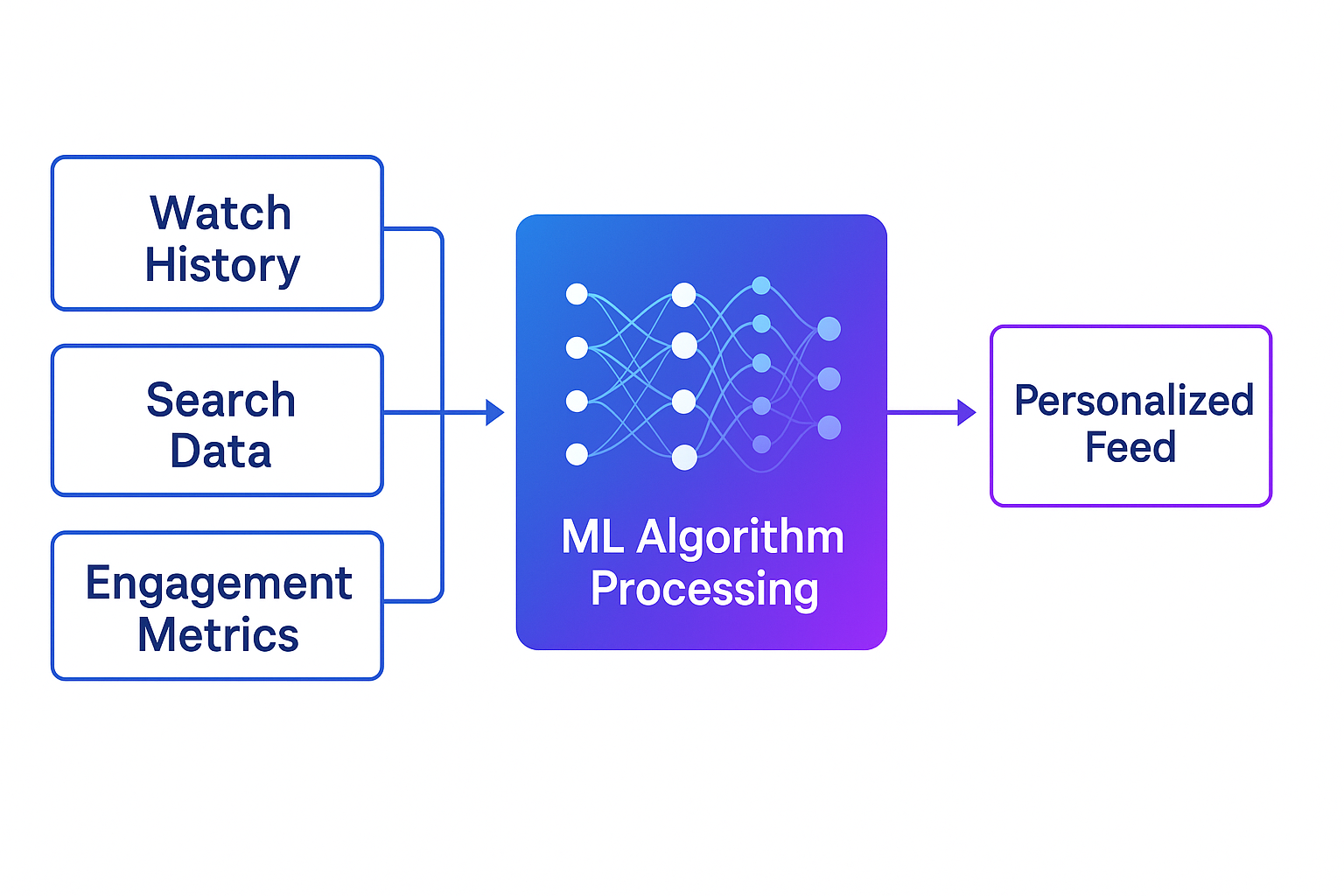
Table of Contents
YouTube’s content delivery system relies on sophisticated machine learning algorithms that analyze user behavior patterns including watch history, search queries, engagement metrics, and demographic data. Content management for standard accounts focuses on training these algorithms rather than implementing hard blocks.
Primary Control Mechanism: Channel Recommendation Filtering
The “Don’t Recommend Channel” feature represents the most effective tool for channel-specific content management on standard YouTube accounts.
Implementation Procedure:
Desktop Web Interface:
- Locate content from the target channel in your Home feed or Suggested Videos
- Select the three-dot menu icon adjacent to the video title
- Choose “Don’t recommend channel” from the dropdown menu
Mobile Applications (iOS/Android):
- Navigate to content from the target channel in your feed
- Tap the three-dot menu icon
- Select “Don’t recommend channel”
Technical Specifications and Limitations:
Scope of Effect: This action removes the specified channel’s content from algorithm-driven recommendation surfaces including:
- Home feed personalized content
- Suggested videos sidebar (Watch Next)
- YouTube Shorts recommendations
- Trending and Explore sections
Known Limitations:
- Does not affect search result visibility
- Does not prevent direct URL access to channel content
- Requires repeated application if new channels emerge with similar content
Management and Persistence: Recommendation preferences are stored in your Google Account activity data. Users can review and modify these settings through:
- Google My Activity dashboard
- YouTube “Not interested” feedback section
- Account-level preference management
This semi-permanent configuration allows for strategic curation while maintaining flexibility for changing content needs.
Secondary Control: Topic-Level Filtering
The “Not Interested” feedback mechanism provides content-type filtering complementary to channel-specific controls.
Strategic Application:
Granular Topic Control: When marking content as “Not Interested,” users should provide specific feedback reasons:
- “I’ve already watched the video” (minimal algorithmic impact)
- “I don’t like the video” (significant topic-level signal)
- “I’m not interested in this topic” (broad category filtering)
Professional Use Cases:
- Segregating professional development content from entertainment
- Maintaining focused research environments
- Preventing algorithm contamination from tangential searches
- Building specialized content profiles for different contexts
Historical Data Management Strategy
YouTube’s recommendation engine fundamentally derives from user behavioral history. Strategic history management provides foundational content control superior to individual channel filtering.
Available Controls and Applications:
| Control Function | Strategic Application | Professional Context |
|---|---|---|
| Pause Watch History | Transitions recommendations from personalized to generalized trending content | Essential for shared devices, classroom environments, or research accounts requiring neutral profiles |
| Clear Watch History | Complete algorithmic reset, removing all historical influence on recommendations | Appropriate when transitioning account purposes or addressing severely misaligned content feeds |
| Pause Search History | Prevents search behavior from influencing recommendations | Critical for preventing off-topic searches from generating unwanted recommendation chains |
| Clear Search History | Removes accumulated search data affecting current recommendations | Useful for resetting topic associations after research projects or temporary interests |
Access Path: Profile Icon → Your data in YouTube → History Settings → YouTube History Management
Strategic Consideration: Pausing both watch and search history effectively converts YouTube from a personalized recommendation platform to a curated trending content service, maximizing user control over exposed content while reducing algorithmic prediction.
Part II: Parental Controls and Supervised Account Management
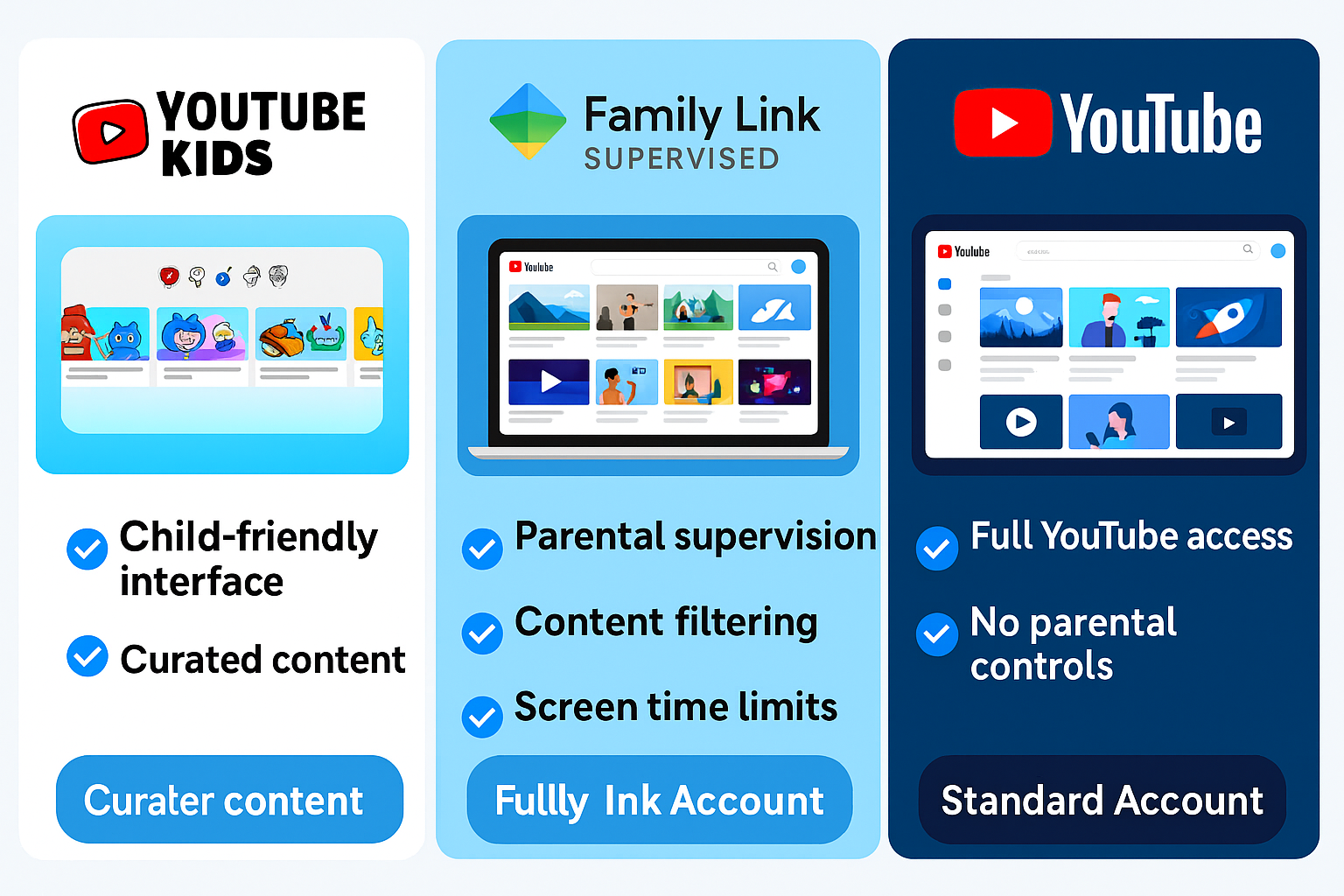
YouTube Kids Platform: Hard Channel Blocking
YouTube Kids represents the only YouTube environment providing permanent channel-level blocking functionality. This dedicated application serves users under age 13 (or applicable regional age threshold) with parent-managed content restrictions.
Channel Blocking Procedures:
Method 1: In-App Blocking (YouTube Kids)
- Locate content from the target channel
- Access the three-dot menu
- Select “Block”
- Complete parental verification (mathematical challenge or custom passcode)
- Confirm “Block entire channel”
Method 2: Parent Account Management (Primary YouTube App)
- Authenticate with linked parent account credentials
- Navigate to target channel page
- Access three-dot menu → “Block channel for kids”
- Select applicable child profile(s) and confirm
Technical Parameters:
- Block applies across all devices logged into the child’s profile
- Block persists until explicit parent-initiated removal
- Block affects only the specific channel; similar content from other sources remains accessible
- Requires continuous parental oversight due to content migration and new channel creation
Enhanced Security Configuration: YouTube Kids offers “Approved Content Only” mode, restricting all viewing to parent-curated channels and videos. This represents the maximum security configuration for youngest users, eliminating algorithmic exposure entirely.
Supervised Accounts via Google Family Link
For users aged 13-17 (or applicable regional thresholds), Google Family Link enables comprehensive parental management of YouTube access on standard accounts.
Available Control Tiers:
Content Setting Levels:
- Explore (Ages 9+): Strictly limited content appropriate for youngest supervised users
- Explore More (Ages 13+): Broader content access while filtering mature themes
- Most of YouTube: Full platform access with age-restricted content filtered
Hard Blocking Capability: Parents with Family Link management can implement permanent channel blocks:
- Navigate to target channel About page
- Select “Report User”
- Choose “Block channel for kids”
- Confirm supervised account(s) for application
Enforcement Characteristics:
- Block applies universally across all devices and sessions
- Block survives account logouts and password changes
- Block remains in effect until parent explicitly removes restriction
- Represents YouTube’s most robust integrated parental control mechanism
Compliance Considerations: Supervised accounts require parent Google Account linkage and active Family Link installation. Organizations deploying supervised accounts for institutional purposes must ensure compliance with COPPA, GDPR Article 8, and applicable regional child data protection regulations.
Part III: Institutional Content Management
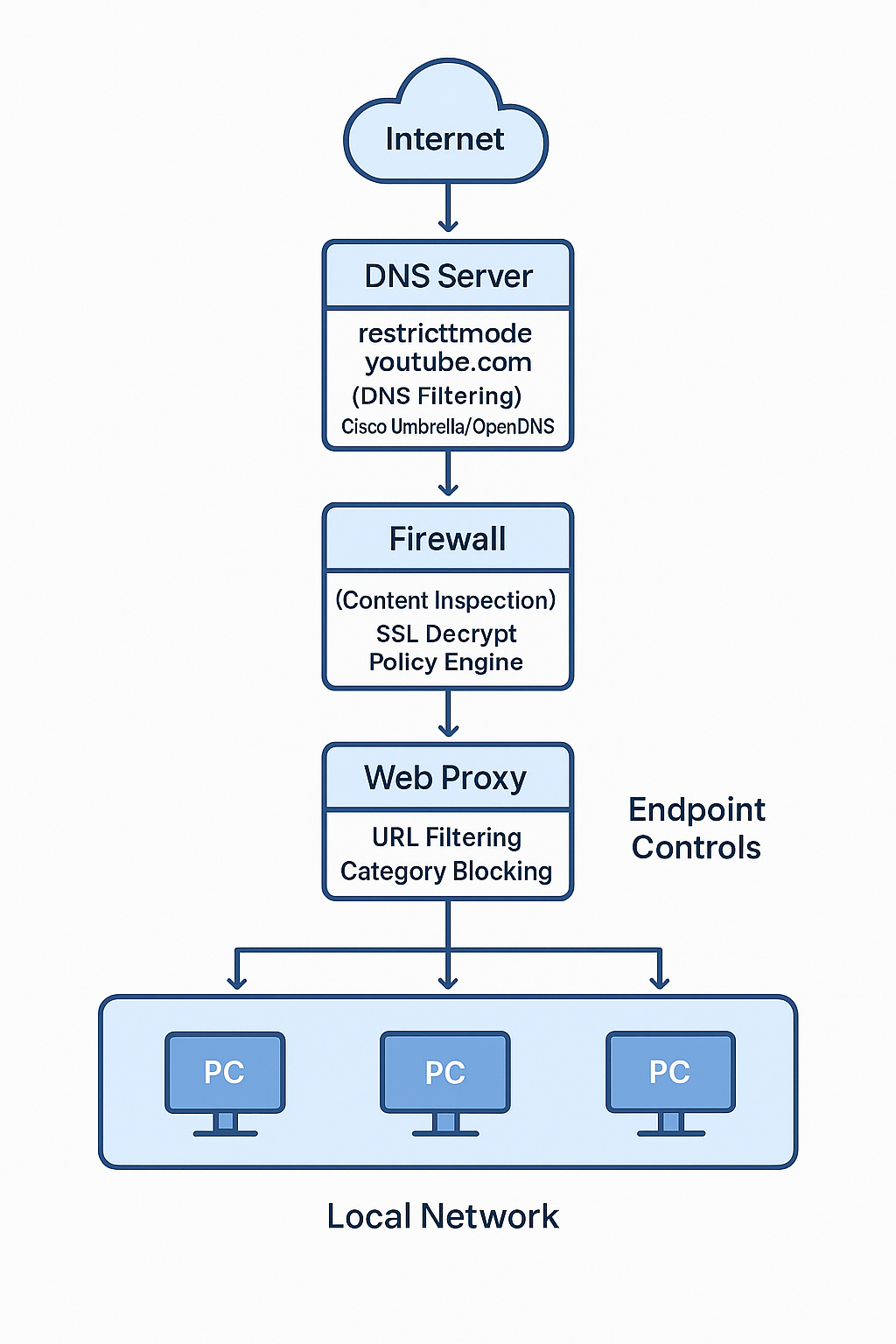
Restricted Mode: System-Level Content Filtering
Restricted Mode employs automated systems, community guideline analysis, and age restriction metadata to filter potentially mature content platform-wide.
Implementation Strategies:
Individual Activation: Profile Icon → Settings → General → Restricted Mode toggle
Characteristics:
- Browser and device-specific (requires activation on each access point)
- User can disable if administrative lock is not applied
- Appropriate for personal voluntary filtering
Network-Level Enforcement (Institutional):
Network administrators can mandate Restricted Mode across entire organizations through:
DNS-Level Implementation: Configure DNS resolution to force YouTube requests through restricted endpoint:
- Standard YouTube:
www.youtube.com - Restricted YouTube:
restrictmoderate.youtube.com
Firewall Policy Configuration: Deploy content filtering rules at network perimeter:
- URL filtering based on YouTube API parameters
- HTTPS inspection with restricted mode enforcement
- Policy-based routing for different user groups
Deployment Context:
- Educational institutions ensuring CIPA compliance
- Corporate environments with acceptable use policies
- Public access facilities (libraries, community centers)
- Healthcare organizations with content appropriateness requirements
Technical Limitations:
- May inadvertently filter legitimate educational content
- Disables comments on all filtered videos
- Effectiveness depends on YouTube’s classification accuracy
- Mobile device users on cellular networks bypass network controls
Advanced Network Architecture for Content Management
Organizations with stringent content governance requirements typically implement multi-layered filtering approaches.
Enterprise-Grade Solutions:
Web Filtering Appliances:
- Cisco Umbrella with YouTube category filtering
- Palo Alto Networks URL filtering with application control
- Fortinet FortiGuard with granular YouTube management
- Zscaler Internet Access with real-time content inspection
Technical Capabilities:
- Category-based blocking (e.g., entertainment, gaming, music)
- Channel-specific whitelist/blacklist management
- URL pattern matching for video ID filtering
- SSL/TLS decryption for HTTPS inspection
- User/group-specific policy application
Managed Browser Policy Implementation:
Group Policy Objects (Windows Domain):
Computer Configuration → Policies → Administrative Templates → Google Chrome → Extensions
- Configure force-installed extension list
- Disable extension modification by users
- Implement YouTube-specific content filtering extensions
Mobile Device Management (MDM):
- Configuration profiles enforcing supervised YouTube access
- Application whitelisting restricting YouTube app installation
- VPN-enforced content filtering for mobile devices
- Containerization separating personal/organizational content
Educational Technology Integration:
Purpose-built EdTech platforms provide curated YouTube access:
- Edpuzzle: Interactive video with teacher-controlled content
- Schoology: Learning management system with embedded YouTube
- Google Classroom: Native YouTube integration with sharing controls
- Canvas LMS: Embedded video with institution-managed libraries
Compliance and Legal Framework:
Institutional content filtering must address:
- FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act): Student data protection in educational contexts
- CIPA (Children’s Internet Protection Act): Mandated filtering for federally funded institutions
- GDPR/ePrivacy Directive: EU requirements for monitoring and data processing disclosure
- State Privacy Laws: California CCPA, Virginia VCDPA, and similar statutes
- Workplace Privacy: Employee notification requirements for network monitoring
Implementation Requirements:
- Transparent acceptable use policies
- User notification of monitoring practices
- Data minimization in logging and reporting
- Regular privacy impact assessments
- Incident response procedures for policy violations
Part IV: Third-Party Tools and Browser Extensions
Security and Privacy Considerations
While browser extensions offer convenience for individual users, organizational deployment requires careful security evaluation.
Risk Assessment Factors:
- Extension permission scope (access to browsing data, site content modification)
- Developer reputation and update frequency
- Code audit availability and third-party security review
- Data collection and transmission practices
- Compatibility with organizational security policies
Vetted Extension Categories:
Content Filtering Extensions:
- Video Blocker: Channel and keyword-based hiding
- Unhook: YouTube interface modification and distraction reduction
- DF Tube: Distraction-free YouTube with granular control
Professional Deployment Protocol:
- Security team evaluation of extension codebase
- Pilot deployment to test group
- Monitoring for compatibility issues and bypass attempts
- Organizational extension repository for approved tools
- Regular security reassessment and version control
Alternative Approach: Managed Bookmarklets For organizations uncomfortable with extensions, JavaScript bookmarklets provide limited functionality without persistent permissions:
- No installation required (saved bookmark with JavaScript code)
- Executes only when user activates
- Limited to current page modification
- Requires user technical literacy for deployment
Part V: Legal and Ethical Frameworks
Copyright and Fair Use Principles
Content filtering does not alter intellectual property rights or usage restrictions.
Key Legal Principles:
Copyright Preservation: Blocking channel recommendations does not:
- Grant license to reproduce or distribute content
- Modify copyright holder’s exclusive rights
- Exempt users from attribution requirements
- Permit commercial use of filtered content
Fair Use Application: Educational and commentary use may qualify for fair use defense, requiring:
- Transformative purpose (criticism, comment, teaching)
- Nature of copyrighted work consideration
- Amount and substantiality of use
- Market effect analysis
Attribution Requirements: Proper attribution remains mandatory regardless of filtering:
- Creator name or channel identification
- Video title and publication date
- Direct link to original content
- Clear distinction between original and derivative work
Mandatory Reporting Obligations
Organizations and individuals encountering harmful or illegal content bear reporting responsibilities beyond personal filtering.
Content Requiring Formal Reporting:
| Violation Category | Reporting Mechanism | Legal Obligation |
|---|---|---|
| Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM) | National Center for Missing & Exploited Children (NCMEC) CyberTipline; Local law enforcement | Federal mandatory reporting (18 U.S.C. § 2258A) |
| Imminent Threats/Violence | Law enforcement immediate contact; YouTube Trust & Safety | Duty to warn in most jurisdictions |
| Hate Speech/Harassment | YouTube Report function; Platform Trust & Safety | Platform Terms of Service enforcement |
| Copyright Infringement | YouTube Copyright Strike system; DMCA takedown notice | Civil remedy, not criminal reporting |
| Misinformation (Health/Elections) | YouTube misinformation reporting; Platform verification | Platform policy enforcement, no legal mandate |
Reporting Procedure:
- Document violation with screenshots and URLs
- Use YouTube’s Report function (three-dot menu → Report)
- Select specific violation category
- Provide detailed description
- Submit to platform for review
- Contact law enforcement if legally required
- Maintain documentation for potential follow-up
Institutional Reporting Protocols: Organizations should establish:
- Designated reporting coordinators
- Escalation procedures for serious violations
- Documentation standards for compliance
- Legal review process for ambiguous cases
- Regular training for staff on reporting obligations
Privacy and Monitoring Disclosure
Organizations implementing content filtering must address privacy implications:
Transparency Requirements:
- Clear acceptable use policies distributed to all users
- Explicit notification of monitoring and filtering practices
- Opt-out procedures where legally required
- Data retention policies for monitoring logs
- Purpose limitation for collected data
Data Protection Compliance:
- GDPR Article 13 transparency obligations
- COPPA parental notice and consent requirements
- State privacy law disclosure obligations
- Workplace privacy statutes (varies by jurisdiction)
Part VI: Strategic Implementation Framework
Needs Assessment and Solution Matching
Effective YouTube content management begins with clear requirement definition:
Personal Use Cases:
- Objective: Algorithmic feed curation without administrative overhead
- Primary Tools: “Don’t recommend channel,” history management
- Implementation: Individual account-level settings
- Maintenance: Periodic review and adjustment
Family/Parental Use Cases:
- Objective: Child safety and age-appropriate content exposure
- Primary Tools: YouTube Kids, Family Link supervised accounts
- Implementation: Parent-managed profiles with active oversight
- Maintenance: Regular content review, block list updates
Educational Institution Use Cases:
- Objective: CIPA compliance, focused learning environment
- Primary Tools: Network-level Restricted Mode, web filtering appliances
- Implementation: IT-managed infrastructure controls
- Maintenance: Policy updates, bypass prevention, audit compliance
Corporate Environment Use Cases:
- Objective: Productivity, bandwidth management, policy enforcement
- Primary Tools: Enterprise web filtering, acceptable use policies
- Implementation: Network security team deployment
- Maintenance: Usage analytics, policy refinement, exception processing
Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Assessment (Weeks 1-2)
- Document current content exposure concerns
- Identify stakeholder requirements (users, parents, administrators)
- Evaluate existing technical infrastructure
- Review legal and compliance obligations
- Define success metrics
Phase 2: Design (Weeks 3-4)
- Select appropriate tools based on use case
- Design technical architecture (if institutional)
- Develop policies and procedures
- Create user documentation
- Plan training requirements
Phase 3: Pilot Deployment (Weeks 5-6)
- Implement controls for test group
- Monitor effectiveness and user feedback
- Identify technical issues and workarounds
- Refine policies based on real-world application
- Document lessons learned
Phase 4: Full Deployment (Weeks 7-8)
- Roll out to complete user population
- Conduct user training sessions
- Establish support resources
- Implement monitoring and reporting
- Create feedback mechanisms
Phase 5: Ongoing Management
- Regular effectiveness review (quarterly)
- Policy updates based on platform changes
- User satisfaction assessment
- Compliance audit preparation
- Continuous improvement initiatives
Performance Metrics and Evaluation
Organizations should establish measurable objectives:
Quantitative Metrics:
- Reduction in inappropriate content exposure incidents
- User satisfaction scores
- Support ticket volume related to content issues
- Compliance audit findings
- Policy violation rates
Qualitative Metrics:
- User perception of safety and appropriateness
- Stakeholder confidence in content governance
- Educational outcomes (for academic institutions)
- Productivity indicators (for corporate environments)
Conclusion: Digital Stewardship in 2025
Effective YouTube content management in 2025 transcends simple blocking mechanisms, requiring strategic approaches matched to specific contexts and requirements. The platform’s algorithmic architecture necessitates understanding recommendation systems and implementing appropriate governance layers.
Key Takeaways:
For Individuals: Content control centers on algorithmic influence through recommendation feedback and strategic history management, creating curated viewing experiences without administrative complexity.
For Parents: Robust tools including YouTube Kids and Family Link supervised accounts provide enforceable protection appropriate to child developmental stages, requiring active oversight and regular review.
For Organizations: Multi-layered approaches combining network infrastructure controls, policy frameworks, and user education deliver compliant, effective content governance aligned with institutional missions.
The evolution from passive content consumption to active digital stewardship represents a fundamental shift in how users, families, and organizations engage with digital media platforms. Success requires ongoing commitment to understanding platform capabilities, maintaining current knowledge of technical controls, and adapting strategies as YouTube’s ecosystem continues evolving.
Additional Resources
Official YouTube Documentation:
- YouTube Help Center: Content Management and Safety
- Google Family Link Support Documentation
- YouTube for Education Resources
Regulatory Guidance:
- FTC COPPA Compliance Information
- EU GDPR Child Protection Guidelines
- FCC CIPA Requirements for Schools and Libraries
Technical References:
- YouTube API Documentation
- Network Filtering Best Practices
- Enterprise Content Management Frameworks
About This Guide
Methodology: This analysis synthesizes official YouTube documentation, regulatory requirements, industry best practices, and technical implementation experience as of October 2025.
Scope: This guide addresses content filtering and management within YouTube’s terms of service. It does not provide guidance on circumventing platform policies or unauthorized access methods.
Updates: YouTube’s features and policies evolve continuously. Users should verify current capabilities through official documentation before implementing controls.
Legal Disclaimer: This guide provides general information for educational purposes. Organizations should consult qualified legal counsel regarding specific compliance obligations and privacy requirements in their jurisdictions.


