Last updated October 2025
Table of Contents
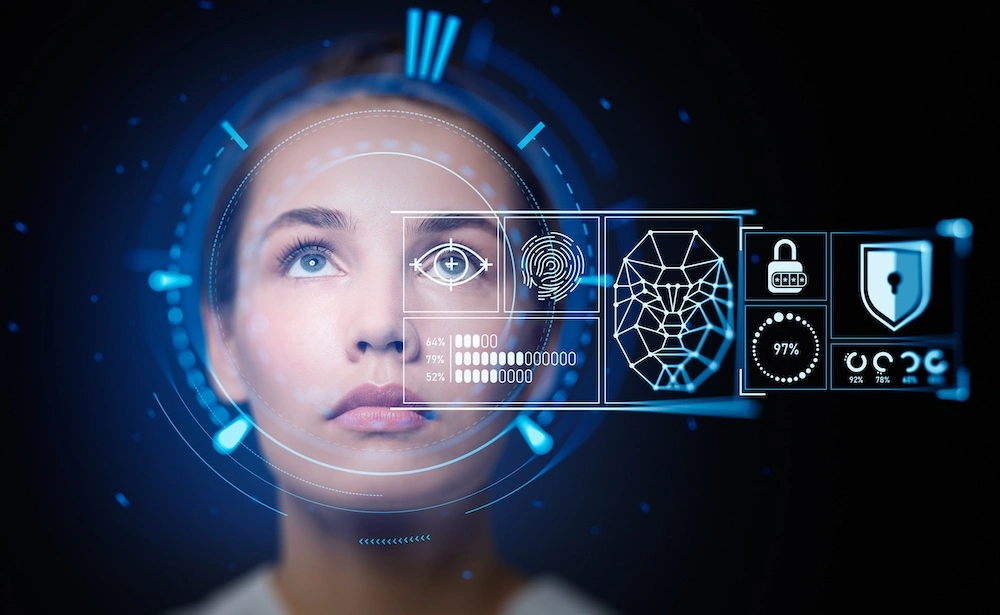
Understanding Image Identification Technology in 2025
Image identification and facial recognition technologies have advanced dramatically, powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning. Understanding how these systems work helps you use them responsibly and interpret results accurately.
How Modern Reverse Image Search Works
Image Analysis: When you upload a photograph, AI algorithms analyze visual elements including colors, patterns, shapes, composition, and unique features.
Feature Extraction: Advanced systems identify key visual markers such as facial structures, landmarks, objects, text, and contextual elements.
Database Comparison: The analyzed image is compared against vast databases containing billions of indexed images from across the web.
Similarity Ranking: Results are ranked by visual similarity, exact matches appearing first, followed by related images.
Metadata Extraction: Systems may extract and display available metadata including file names, locations, dates, and associated text from web pages where images appear.
Facial Recognition Technology
Modern facial recognition operates through several sophisticated steps:
Face Detection: AI identifies human faces within images, even in crowded or complex scenes.
Facial Landmark Mapping: Systems map specific points on faces (eyes, nose, mouth, facial contours) creating a unique facial signature.
Feature Analysis: Algorithms measure distances between facial features, creating a mathematical representation called a “faceprint.”
Database Matching: The faceprint is compared against databases to find potential matches.
Confidence Scoring: Results are provided with confidence levels indicating match probability.
Important Limitations
Accuracy Challenges:
- Facial recognition accuracy varies based on image quality, lighting, angles, and facial expressions
- Systems show documented bias, particularly struggling with darker skin tones and certain ethnicities
- Makeup, aging, facial hair, and accessories significantly affect accuracy
- Low-resolution images produce unreliable results
False Positives: Facial recognition systems can incorrectly identify individuals, particularly with limited or poor-quality source images. Never make important decisions based solely on automated identification.
Privacy Limitations: Most facial recognition tools cannot search private social media content, password-protected sites, or databases not publicly indexed.
Top Methods to Identify People in Pictures (2025)
Method 1: Reverse Image Search with Google Lens

Google Lens has evolved into the most comprehensive and accessible image identification tool, combining reverse image search with advanced AI object and face recognition.
Why Google Lens Leads:
Google Lens helps you explore similar images effortlessly, allowing you to search by image and discover results across multiple categories. Its integration with Google’s massive search index and continuous AI improvements make it the first choice for most users.
How to Use Google Lens:
On Desktop:
- Visit Google Images
- Click the camera icon in the search bar
- Upload your image or paste an image URL
- Review results showing:
- Exact matches of the image
- Visually similar images
- Web pages containing the image
- Related images and information
On Mobile (Android/iOS):
- Open the Google app or download Google Lens app
- Tap the camera icon
- Either upload a photo from your library or take a new picture
- Select specific elements within the image for focused searches
- Use the “Search” button to find matches
Advanced Features:
- Text recognition and translation within images
- Object identification for shopping
- Plant and animal species identification
- Landmark and location recognition
- QR code and barcode scanning
Best For: General image identification, finding image sources, locating similar images, and accessing the broadest search index.
Privacy Note: Google Lens analyzes uploaded images and may retain data according to Google’s privacy policy. Review Google’s terms before uploading sensitive content.
Method 2: TinEye Reverse Image Search

TinEye is probably the oldest and most well-known reverse image search engine and reverse pic lookup service, focusing specifically on tracking where images appear across the web.
TinEye’s Specialized Approach:
Unlike general search engines, TinEye specializes in image provenance—showing exactly where specific images have been published, when they first appeared, and how they’ve been modified over time.
Key Features:
- Searches over 63 billion images (as of 2025)
- Shows where images are currently used online
- Provides upload dates and modification history
- Identifies cropped, edited, or resized versions
- Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge browser extensions
- API access for developers and businesses
- Alerts for new appearances of your images (paid feature)
How to Use TinEye:
- Visit TinEye.com
- Upload your image or paste an image URL
- Review results showing websites using the image
- Sort by “Best Match,” “Most Changed,” “Biggest Image,” “Newest,” or “Oldest”
- Click results to visit source pages
Best For: Copyright protection, tracking image usage, finding original sources, and verifying image authenticity.
Business Applications: TinEye offers enterprise plans for brands protecting intellectual property and monitoring unauthorized image use.
Method 3: PimEyes Face Recognition Search
PimEyes is an advanced face recognition search engine, a reverse image search tool, and a photo search mechanism used to find which websites publish your photos online.
Understanding PimEyes:
PimEyes specializes exclusively in facial recognition, searching the open web (excluding social media) to find where faces appear online. This powerful tool raises significant privacy implications and should be used responsibly.
How PimEyes Works:
- Upload a clear photo of a face
- PimEyes analyzes facial features creating a unique faceprint
- The system searches indexed public web pages for similar faces
- Results show potential matches with confidence scores
Features:
- Searches specifically for human faces
- Works with various photo qualities and angles
- Handles multiple faces in single images
- Provides facial match confidence percentages
- Alert system for new images (premium feature)
- Image removal requests for privacy protection
Subscription Tiers:
- Free Search: Limited searches with blurred results
- Open Plus: Access to source links ($29.99/month)
- PROtect: Enhanced features including alerts and image removal assistance (starting $89.99/month)
Critical Ethical Note: PimEyes is controversial due to privacy concerns. The service explicitly states it should only be used to find your own images online, not to surveil others. Misuse for stalking, harassment, or privacy invasion is unethical and potentially illegal.
Best For: Monitoring your own online presence, protecting personal privacy, and identifying unauthorized use of your own photos.
Visit PimEyes (Use Responsibly)
Method 4: Lenso.ai Visual Search
Lenso.ai is the best reverse image search website for anyone looking for people, places, duplicates and related/similar photos, offering the biggest variety of results and indexing countless pictures daily.
Lenso.ai’s Comprehensive Approach:
Lenso.ai combines traditional reverse image search with AI-powered categorization, making it easier to find specific types of content.
Search Categories:
- People: Find images containing similar individuals
- Places: Identify locations and landmarks
- Duplicates: Find exact or near-duplicate images
- Related Images: Discover contextually similar content
- Similar: Locate visually similar images
Key Features:
- Advanced filtering options
- Sort by best/worst match, newest/oldest
- Exact URL specification
- Keyword-based refinement
- Works across all major browsers and devices
- Regular database updates
How to Use Lenso.ai:
- Visit Lenso.ai
- Upload your image or paste a URL
- Select your search category (People, Places, etc.)
- Apply filters to refine results
- Sort results by relevance, date, or quality
Best For: Comprehensive searches across multiple categories, finding people in various contexts, location identification.
Method 5: Bing Visual Search
Microsoft’s Bing Visual Search provides another powerful alternative with unique features that complement Google’s offerings.
Bing Visual Search Advantages:
Unique Features:
- “Text Mode” allows selecting and searching specific text within images
- Shopping integration for product identification
- Strong performance with celebrities and public figures
- Alternative index when Google doesn’t return results
- Clean, intuitive interface
How to Use Bing Visual Search:
- Visit Bing Visual Search
- Click the camera icon or visit directly
- Upload your image or provide a URL
- Review categorized results:
- Related images
- Web pages containing the image
- Shopping results for similar items
- Celebrity or public figure identification
Additional Capabilities:
- Integration with Microsoft Edge browser
- Mobile app with camera search
- Object detection within images
- Color and pattern-based search refinement
Best For: Alternative search when Google doesn’t provide results, shopping and product identification, accessing Microsoft’s unique index.
Method 6: Yandex Images
Yandex, Russia’s largest search engine, offers powerful reverse image search with particularly strong results for Eastern European and Russian content.
Yandex Strengths:
Unique Advantages:
- Excellent facial recognition capabilities
- Strong index of Eastern European web content
- Finds results other search engines miss
- Advanced filters by size, color, type, and layout
- Free and unlimited searches
How to Use Yandex Images:
- Visit Yandex Images
- Click the camera icon
- Upload your image or paste URL
- Review results with translations (automatic for non-Russian speakers)
Limitations:
- Interface and some results in Russian (though Chrome can translate)
- Privacy concerns due to Russian data jurisdiction
- Less comprehensive outside Eastern Europe and Russia
Best For: Finding people or images with Eastern European connections, alternative perspective when Western search engines fail.
Privacy Warning: Be aware of data jurisdiction and privacy implications when using services based in different countries.
Method 7: Social Catfish (Specialized Identity Verification)
Social Catfish focuses specifically on online dating and romance scam prevention through image verification.
Targeted Verification Service:
Social Catfish specializes in helping people verify the identity of individuals they meet online, particularly on dating platforms and social media.
Services Offered:
- Reverse image search across dating sites
- Social media profile verification
- Background checks and public records
- Phone and email lookup
- Comprehensive identity reports
How It Works:
- Sign up for Social Catfish service
- Upload photo or provide profile information
- Service searches across dating sites, social media, and public records
- Receive detailed report on findings
Pricing: Subscription-based service, typically $5.99 for trial, then $27.48/month
Best For: Online dating safety, verifying potential romantic partners, identifying catfish attempts, romance scam prevention.
Note: This is a paid service specializing in personal safety and online relationship verification rather than general image search.
Method 8: FaceCheck.ID (Social Media Focus)

FaceCheck.ID specializes in finding social media profiles through facial recognition.
Social Media Specialization:
While most facial recognition tools avoid social media due to privacy and terms of service issues, FaceCheck.ID focuses on publicly accessible profiles.
Features:
- Searches across multiple social media platforms
- Free tier with limited searches
- Finds public profiles and pages
- Works with various photo qualities
Important Limitations:
- Only searches publicly accessible content
- Cannot access private profiles or restricted content
- Accuracy varies significantly
- Results depend on profile privacy settings
Best For: Finding public social media profiles, connecting with people you’ve met but whose names you don’t remember.
Ethical Use Only: Should only be used to find your own profiles or reconnect with people who would welcome contact, never for surveillance or harassment.
Step-by-Step: How to Identify Someone in a Picture
Preparation Steps
1. Assess Your Image Quality:
Better source images produce better results. Ideal characteristics include:
- Clear, well-lit photograph
- Face visible and unobscured
- High resolution (at least 500×500 pixels)
- Minimal motion blur
- Neutral expression (if searching for a person)
If your image is poor quality, consider:
- Using photo enhancement tools first
- Trying multiple variations of the image
- Cropping to focus on specific elements
2. Determine Your Search Goal:
Clarify what you’re trying to accomplish:
- Finding the original source of an image?
- Identifying a person in the photograph?
- Locating where an image has been used online?
- Verifying someone’s claimed identity?
Your goal determines which tool and approach to use.
3. Gather Context:
Note any available context that might help:
- When/where was the photo taken?
- What platform did you find it on?
- Any associated text or captions?
- Other identifying information visible in the image?
Search Process
Step 1: Start with Google Lens
Begin with the most comprehensive tool:
- Upload your image to Google Lens
- Review all results carefully
- Check “Visually similar images”
- Examine web pages where the image appears
- Note any names, locations, or context provided
Step 2: Try TinEye for Verification
Cross-reference with TinEye:
- Upload the same image to TinEye
- Sort by “Oldest” to find the original source
- Check modification history
- Verify dates and sources
Step 3: Use Specialized Tools if Needed
If general search doesn’t work:
- For faces: Try PimEyes or Lenso.ai (People category)
- For Eastern European content: Try Yandex
- For product identification: Use Bing Visual Search
- For dating profiles: Consider Social Catfish
Step 4: Analyze Results Critically
Don’t accept results at face value:
- Verify information across multiple sources
- Check confidence scores on facial recognition results
- Look for context clues that confirm or contradict identification
- Be skeptical of single-source results
Step 5: Respect Privacy and Act Ethically
Before taking action:
- Consider whether your identification respects privacy
- Evaluate if contacting the person is appropriate
- Never share identified information publicly
- Respect the person’s right to anonymity if that’s their choice
Troubleshooting Common Issues
No Results Found:
- Try different reverse image search tools
- Crop the image to focus on specific elements
- Try higher quality versions if available
- Search for similar images rather than exact matches
Too Many Irrelevant Results:
- Use more specific search tools (face-focused vs. general)
- Add contextual keywords when available
- Focus search on particular categories (Lenso.ai)
- Refine by date, size, or other filters
Contradictory Results:
- Verify information independently
- Look for the earliest/most authoritative source
- Check multiple tools for consistency
- Treat uncertain results with skepticism
Privacy Concerns:
- Use tools that don’t require account creation
- Review privacy policies before uploading sensitive images
- Consider cropping images to show only necessary elements
- Delete search history if the tool allows
Practical Use Cases and Best Practices
Personal Safety and Romance Scam Prevention
Scenario: You’ve met someone online and want to verify their identity before meeting in person or developing a relationship.
Best Practices:
- Use Multiple Tools: Cross-reference results from Google Lens, TinEye, and specialized services like Social Catfish
- Look for Consistency: Verify that the person’s story matches what you find online
- Check for Stock Photos: Scammers often use stock photography or stolen images
- Reverse Search Multiple Photos: If someone provides several pictures, search each one
- Video Chat First: Request a live video call as additional verification
- Trust Your Instincts: If something feels wrong, proceed cautiously
Red Flags:
- Images appear on multiple different profiles with different names
- No social media presence despite claiming to be active online
- Reluctance to video chat or meet in person
- Found images appear in modeling portfolios or stock photo sites
- Results show the images are associated with scam warnings
Copyright Protection for Creators
Scenario: You’re a photographer or artist wanting to find unauthorized uses of your work.
Best Practices:
- Regular Monitoring: Set up alerts with TinEye or PimEyes to notify you of new uses
- Document Everything: Screenshot and save evidence of unauthorized use
- Check Licensing: Determine if uses are properly licensed or within fair use
- Send DMCA Takedowns: File formal takedown notices with platforms hosting unauthorized content
- Consider Watermarking: Add visible or invisible watermarks to track your work
- Professional Help: Consult intellectual property attorneys for significant infringements
Tools Specifically for Copyright Protection:
- TinEye (with alerts)
- Pixsy (specializes in image theft for photographers)
- Google Alerts for your name/business
- Copyright Claims Board (US) for formal complaints
Journalism and Fact-Checking
Scenario: You’re verifying the authenticity and source of news images or checking for manipulated media.
Best Practices:
- Verify Original Source: Use TinEye to find earliest appearance and original publisher
- Check for Manipulation: Look for signs of editing, cropping, or context removal
- Cross-Reference: Verify with multiple search tools
- Examine Metadata: Check EXIF data if accessible for date, location, camera info
- Contact Sources: Reach out to original photographers or witnesses
- Document Process: Keep records of verification steps for transparency
Additional Tools for Journalists:
- InVID (video verification plugin)
- FotoForensics (detects image manipulation)
- Jeffrey’s Image Metadata Viewer (EXIF data analysis)
Genealogy and Family History Research
Scenario: You’re researching family history and trying to identify people in old photographs.
Best Practices:
- Start Broad: Use general reverse image search for any identifying information
- Historical Archives: Check specialized genealogy sites and historical photo databases
- Social Media: Join genealogy groups and forums for identification help
- Compare with Known Photos: Use facial recognition to compare with confirmed relatives
- Document Everything: Record where each photo was found and any associated information
- Collaborate: Work with relatives who may recognize individuals
Specialized Resources:
- Ancestry.com (historical photo collection)
- FamilySearch (free genealogy records and photos)
- Genealogy forums and Facebook groups
- Local historical societies and archives
Future of Image Identification Technology
Emerging Technologies (2025 and Beyond)
Advanced AI and Machine Learning:
- More accurate facial recognition with reduced bias
- Better handling of occlusions, angles, and poor lighting
- Real-time video search capabilities
- Multi-modal search combining images, video, and audio
3D Face Recognition:
- Depth-sensing cameras creating 3D face maps
- Superior accuracy compared to 2D systems
- Better resistance to spoofing and deepfakes
- Integration with AR/VR platforms
Edge Processing:
- On-device facial recognition without cloud uploads
- Enhanced privacy through local processing
- Faster results with reduced latency
- Reduced dependency on internet connectivity
Blockchain Verification:
- Immutable records of image authenticity
- Photographer attribution and licensing tracking
- Proof of original creation date
- Protection against manipulation and deepfakes
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies
Facial Recognition Blockers:
- AI-generated adversarial patterns that confuse facial recognition
- Privacy-focused makeup and accessories
- Clothing designed to disrupt recognition algorithms
Decentralized Search:
- Peer-to-peer image search without centralized databases
- User-controlled data sharing
- Privacy-first architecture
Differential Privacy:
- Search capabilities that protect individual privacy
- Aggregated results without exposing specific individuals
- Balance between utility and privacy protection
Regulatory Evolution
Expected Developments:
- Stricter regulations on commercial facial recognition
- International standards for biometric data protection
- Increased transparency requirements for AI systems
- Right-to-know when you’ve been identified by automated systems
Critical Legal and Ethical Disclaimer
IMPORTANT: This guide is for educational and legitimate purposes only. Using image identification and facial recognition technologies carries significant legal, ethical, and privacy implications that must be understood before use.
Legitimate Use Cases ONLY:
- Personal Safety: Verifying the identity of someone you’re communicating with online to prevent catfishing or romance scams
- Copyright Protection: Identifying unauthorized use of your own photographs
- Research Journalism: Fact-checking images for news verification purposes
- Finding Lost Persons: Assisting in locating missing individuals through proper channels
- Personal Property: Identifying people in your own photographs from events you attended
- Art Attribution: Finding artists or photographers for proper credit and licensing
- Genealogy Research: Identifying relatives in historical family photographs
PROHIBITED and Illegal Uses:
- Stalking or harassment of any individual
- Doxxing (publishing private information without consent)
- Surveillance of individuals without their knowledge or consent
- Employment discrimination based on social media images
- Bypassing privacy settings on social media platforms
- Creating deepfakes or manipulated images for deception
- Identity theft or impersonation
- Invasion of privacy for malicious purposes
Legal Considerations:
Privacy Laws: Many jurisdictions have strict privacy and data protection laws (GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, BIPA in Illinois) that regulate facial recognition and image use.
Consent Requirements: Using someone’s image or identifying them through photos may require their consent depending on context and jurisdiction.
Copyright: Photographs are automatically copyrighted by their creators. Respect image rights and fair use limitations.
Terms of Service: Many social media platforms prohibit scraping images or using automated tools to identify users.
Children’s Privacy: Extra legal protections exist for minors (COPPA in the US, GDPR-K in Europe). Never use these tools to identify children without proper authority.
Best Practices:
- Only search for people with legitimate reasons
- Respect individuals’ privacy and right to anonymity
- Never share identified information publicly without consent
- Be aware of biases and errors in automated identification systems
- Consider the ethical implications before taking action based on identification results
- When in doubt, consult legal professionals
This guide provides information about available technologies. Users are solely responsible for ensuring their use complies with applicable laws and ethical standards.
FAQs
Can I find someone using only their picture?
Yes, most reverse image search tools work by simply uploading an image in the search bar or copying and pasting the image URL in the search bar, then searching the web and database for where that specific image appears. However, success depends on whether the person’s image appears in publicly indexed online content. Private social media profiles, unindexed websites, and offline photos cannot be searched. Always use these capabilities ethically and legally.
What is the easiest way to identify people in pictures?
Google Lens is the most accessible and easiest tool for beginners. Simply visit Google Lens, upload your image, and review results showing similar images, web pages containing the image, and related information. For facial recognition specifically, tools like PimEyes or Lenso.ai provide more targeted results, though they require careful, ethical use.
Are facial recognition search tools accurate?
Facial recognition accuracy varies significantly based on image quality, lighting, angles, and the individual’s skin tone. Modern systems achieve 95-99% accuracy under ideal conditions with high-quality images of people with lighter skin tones. However, accuracy drops substantially with poor images and shows documented bias against darker skin tones, women, and certain ethnic groups. Always verify results and never rely solely on automated identification for important decisions.
Is it legal to use facial recognition tools to identify strangers?
Legality depends on jurisdiction and intended use. Using publicly available tools to search publicly indexed content is generally legal, but using results for harassment, stalking, discrimination, or privacy invasion is illegal. Many jurisdictions have specific biometric privacy laws (like Illinois’ BIPA) that restrict how facial recognition data can be collected and used. Always research applicable laws and use these tools only for legitimate purposes.
Can I identify someone from a photo on Instagram or Facebook?
Directly searching private social media content is generally not possible, as platforms protect user privacy by blocking automated scraping. However, if someone’s photos appear on public profiles, business pages, or websites outside of social media, reverse image search may find them. Attempting to bypass platform privacy protections violates terms of service and may be illegal.
How do I protect my own photos from being identified?
To protect your privacy: adjust social media privacy settings to limit public visibility, avoid posting high-resolution face photos publicly, consider using facial recognition blocking technology (specialized patterns or makeup), watermark important images, regularly search for your own images to monitor usage, and submit removal requests to search engines and facial recognition services when you find unwanted results.
What should I do if I’m being stalked using these tools?
If you believe someone is using facial recognition or image search to stalk or harass you: document all evidence, report to law enforcement (particularly if threats are involved), contact platform support to report harassment, request removal from facial recognition databases (PimEyes offers removal service), consider legal action including restraining orders, adjust all privacy settings to maximum protection, and consult with privacy attorneys or victim advocacy organizations.
Can these tools identify people in old or historical photos?
Identification of people in old photographs is challenging. Reverse image search can find where historical photos appear online (archives, genealogy sites, historical societies). However, facial recognition is less effective with old photos due to image quality, different photographic processes, aging of subjects, and limited indexed historical content. Genealogy-specific tools and communities often provide better results than general search engines.
How much does image identification technology cost?
Many tools offer free tiers: Google Lens is completely free, TinEye offers free searches with limited features, Bing Visual Search is free, and Yandex Images is free. Specialized tools have subscription models: PimEyes starts at $29.99/month, Social Catfish costs approximately $27.48/month, and enterprise versions of TinEye and other services range from hundreds to thousands of dollars annually. For most personal uses, free tools are sufficient.
What’s the difference between reverse image search and facial recognition?
Reverse image search finds where specific images appear online and locates visually similar images by analyzing overall visual characteristics. Facial recognition specifically identifies human faces within images by analyzing facial features and comparing against databases of faces. Google Lens combines both approaches, while tools like PimEyes focus exclusively on facial recognition. Reverse image search is broader and less privacy-invasive, while facial recognition is more specific but raises greater ethical concerns.
Conclusion: Responsible Image Identification in 2025
Image identification and facial recognition technologies have become powerful tools that, when used responsibly, serve legitimate purposes from personal safety to copyright protection. However, these same technologies pose significant risks to privacy, civil liberties, and personal security when misused.
Key Takeaways:
Technology is Powerful: Modern AI-powered tools can identify people and track images across the internet with unprecedented accuracy, making it easier than ever to find information about images and the people in them.
Legal Compliance is Essential: Privacy laws vary by jurisdiction but increasingly protect individuals’ biometric data and images. Always understand applicable laws before using identification tools.
Ethics Matter More Than Legality: Even when technically legal, many uses of facial recognition and image identification are ethically questionable. Always consider whether your search respects privacy and dignity.
Accuracy Isn’t Guaranteed: Facial recognition systems make mistakes, show bias, and produce false positives. Never make important decisions based solely on automated identification without verification.
Context is Critical: The same tool used for personal safety (verifying an online date) or copyright protection (finding stolen photos) can also be misused for stalking or harassment. Your intentions and actions determine whether use is appropriate.
Privacy Protection Matters: As these tools become more powerful, protecting your own privacy becomes increasingly important. Use privacy settings, consider your digital footprint, and monitor for unauthorized use of your images.
The Future Requires Vigilance: As technology advances, the balance between legitimate uses and privacy protection will continue to challenge individuals, businesses, and lawmakers. Stay informed about both capabilities and regulations.
Best Practices Moving Forward:
- Use the minimum necessary tool for your legitimate purpose
- Verify results through multiple sources before drawing conclusions
- Respect privacy and consider how identification might affect others
- Know the law in your jurisdiction and comply with regulations
- Prioritize consent and obtain permission when possible
- Protect your own privacy by limiting public image exposure
- Report misuse of these tools to appropriate authorities
- Stay informed about evolving technology and regulations
Image identification technology will continue advancing, bringing both benefits and challenges. By using these tools responsibly, respecting privacy, complying with laws, and considering ethical implications, we can harness their benefits while protecting fundamental rights to privacy and dignity in our increasingly visual digital world.
This guide is for educational purposes and reflects the state of image identification technology as of 2025. Laws, regulations, and technologies continue evolving. Always verify current legal requirements in your jurisdiction before using image identification tools. This article does not constitute legal advice—consult qualified legal professionals for specific situations.
See also: How to Use ChatGPT and Gemini Effectively (2025 Guide)


