Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) are integral to efficient business operations, yet distinctions between the two are crucial. You might ask yourself, “What is the difference between MRP and ERP software?”
MRP focuses on production needs and managing resources, while ERP extends its scope, integrating diverse business processes. Unraveling these disparities is vital for businesses navigating the complex realm of resource management.
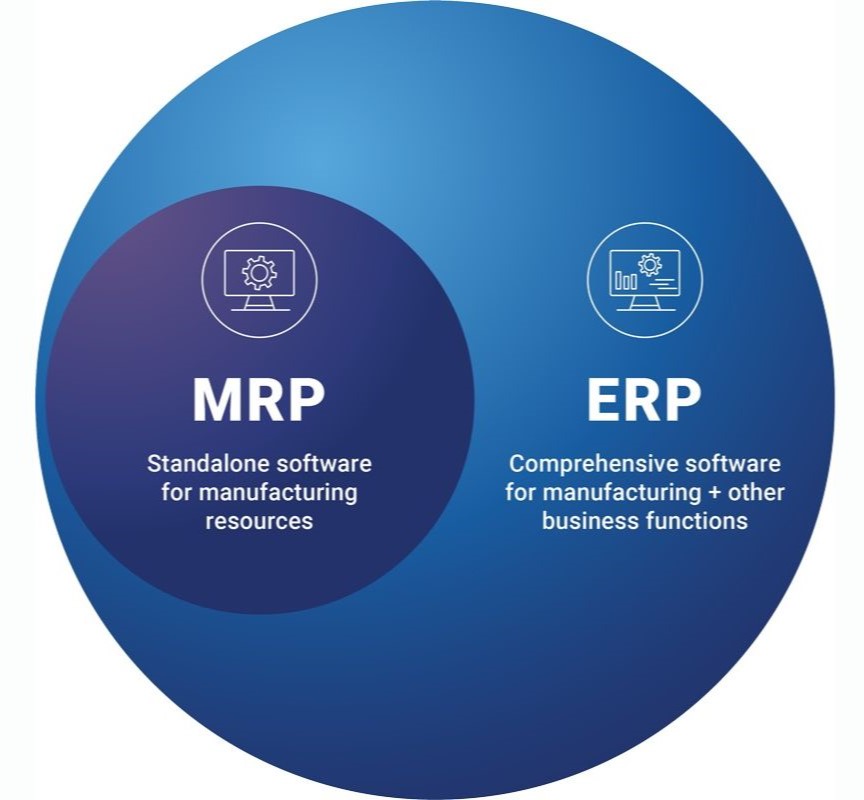
MRP (Manufacturing Resource Planning) primarily addresses production needs, managing inventory, and scheduling. In contrast, ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) encompasses MRP functionalities but extends further, integrating diverse business processes like finance and HR. ERP provides a comprehensive, interconnected solution, making it broader in scope compared to the more focused MRP system.
Reading an article on what is the difference between MRP and ERP software
is essential for businesses seeking streamlined operations. It unravels nuanced distinctions, aiding decision-makers in selecting the right software. Additionally, understanding how MRP’s focused production approach differs from ERP’s comprehensive integration ensures informed choices, optimizing resource management, and fostering organizational efficiency. Also, check out our top picks on innovative business ideas related to graphic design!
See Also: 8 Great Micro SaaS Ideas Your Business Can Implement Real Fast
Table of Contents
Overview of MRP Software
Manufacturing Resources Planning (MRP) frameworks urgently oversee producing processes proficiently. These frameworks coordinate different viewpoints, principally zeroing in on stock administration and creation booking.
Characterizing MRP Frameworks
MRP frameworks smooth out the obtainment and utilization of manufacturing fundamentals for creation.
Moreover, by breaking down interest, these frameworks upgrade stock levels, guaranteeing harmony in the organic market.
Essential Concentration: Assembling Cycles
The central strength of MRP programming lies in its capacity to synchronize producing activities.
It works with exact creation Planning, guaranteeing Resources are distributed productively and creation plans are met.
Advantages of MRP Programming
Executing MRP programming yields significant advantages. Further developed stock administration lessens conveying expenses and improves independent direction.
Continuous information openness enables associations to answer quickly to advertise changes, improving functional dexterity.
Drawbacks: Expenses and Intricacy
Be that as it may, embracing MRP arrangements accompanies difficulties. High execution expenses and framework intricacy can present obstacles for certain organizations.
The underlying Enterprise and the expectation to learn and adapt related to these frameworks require cautious thought.
All in all, while MRP programming fundamentally further develops fabricating productivity and direction, associations should gauge the benefits against the related expenses and intricacies before reception.
Overview of ERP Programming
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) frameworks are critical in improving hierarchical productivity and combination.
These far-reaching programming arrangements are intended to smooth out different business processes, giving a bound-together stage to overseeing assorted capabilities.
Characterizing ERP Frameworks
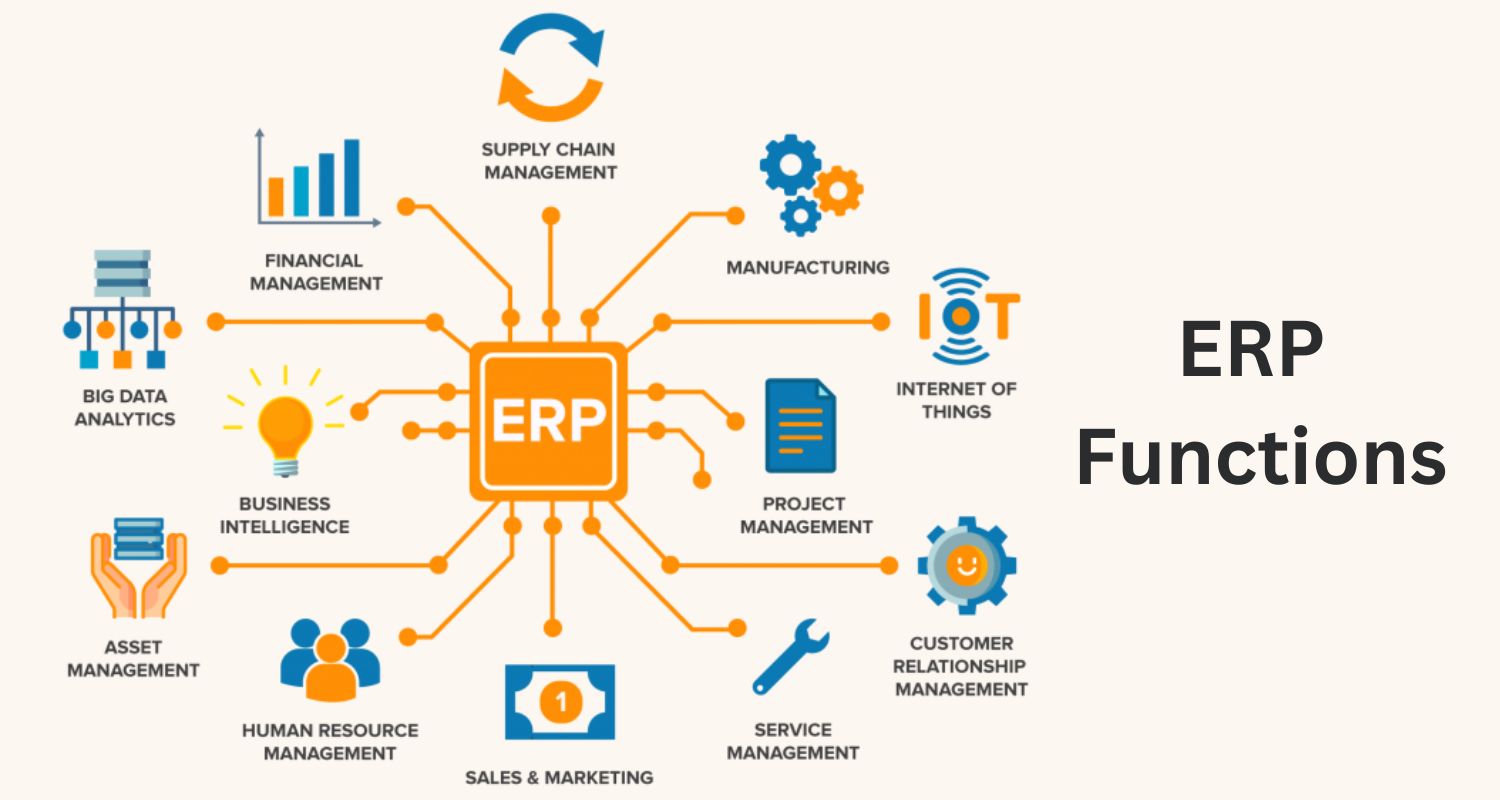
ERP frameworks are concentrated information bases that incorporate and smooth out many business processes across divisions.
From bookkeeping and client relationships with the board (CRM) to inventory networks with the executives, ERP programming is expected to provide a comprehensive way to deal with business tasks.
Extensive variety of Uses
The flexibility of ERP frameworks reaches out across various business regions.
They are a unified center point for monetary information, client connections, and production network exercises.
This interconnectedness guarantees that data streams flawlessly across the association.
Benefits of ERP Programming
Carrying out ERP programming yields various benefits. Further developed effectiveness is accomplished through smoothed-out cycles and information openness.
Informed independent direction is more open as constant information is promptly accessible, empowering a more responsive way to deal with changing business conditions.
Drawbacks: Expenses and Intricacy
Notwithstanding its advantages, ERP execution accompanies difficulties. High starting expenses concerning programming and preparing can be a huge hindrance.
The intricacy of coordinating ERP across different capabilities likewise represents a possible hindrance, requiring cautious preparation and execution.
Considering ERP programming offers extensive answers for different business needs, associations must gauge the benefits against the related expenses and intricacies before embracing these frameworks.
What is the Difference Between MRP and ERP Software
Planned Client Bases and Enterprises
- Manufacturing Necessities Planning (MRP) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) frameworks serve particular client bases and Enterprises.
- MRP frameworks target fabricating enterprises, zeroing in on advancing creation cycles and stock administration.
- Interestingly, ERP frameworks have a more extensive degree of taking special care of different businesses, including assembly, money, and administration.
Works and Highlights: Modules Outline
- MRP frameworks are specific, focusing on Manufacturing preparation and stock control. They frequently incorporate modules like Expert Creation Planning (MPS) and Bill of Manufacturers (BOM).
- ERP frameworks, being more thorough, include a more extensive scope of capabilities. Instances of ERP modules incorporate Bookkeeping, Client Relationship The board (CRM), and Inventory network The executives (SCM).
- ERP’s coordinated methodology interfaces these modules, giving an all-encompassing perspective on hierarchical cycles.
Intricacy and Coordination Abilities
- MRP frameworks are known for their effortlessness, zeroing in on unambiguous assembling perspectives. They give viable answers for organizations with direct creation needs.
- Conversely, ERP frameworks are more intricate because of their far-reaching functionalities. ERP’s solidarity lies in its capacity to coordinate assorted business capabilities, empowering consistent correspondence across divisions.
- This intricacy is useful for associations requiring a bound-together stage for multi-layered tasks.
Execution Expenses
- While considering execution costs, MRP frameworks, by and large, have lower forthright costs. They are intended for organizations with explicit assembling necessities, settling on a savvy decision for designated needs.
- Then again, ERP execution includes greater expenses because of its far-reaching nature and more extensive application.
- The speculation incorporates programming as well as preparing and potential customizations, given the association’s intricacy.
Which One is Appropriate for Your Business?
Now that we have an answer to “What is the difference between MRP and ERP software
” let’s discuss which one is right for your business. Picking between Manufacturing Resources Planning (MRP) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) relies upon different variables custom-fitted to your business needs.
Consider Business Size and Size of Tasks
Manufacturing ERP software may be ideal for more modest organizations with clear assembling needs. Its effortlessness adjusts well to the size of activities, giving effective arrangements without pointless intricacy.
Bigger Enterprises managing complex activities and different divisions may find ERP more reasonable. The exhaustive idea of ERP obliges the intricacies of bigger-scope organizations.
Assess Spending Plan Requirements
Spending plan contemplations assume a vital part in the dynamic cycle. For the most part, Katana MRP frameworks accompanied lower forthright expenses, making them financial plans well disposed of for more modest organizations.
Conversely, ERP execution includes a higher introductory Enterprise because of its extensive functionalities.
Consider your financial plan limitations cautiously, gauging the expense against the drawn-out advantages and adaptability of the picked framework.
Represent Explicit Industry Necessities
Industry-explicit requirements are central. MRP frameworks are custom-made for assembling enterprises, giving centered answers for the creation and stock administration.
ERP’s adaptability becomes worthwhile if your business works in areas past making, for example, money or administration.
Assess how well the picked framework lines up with the special necessities of your industry.
Check out this guide on t-shirt printing machines!
Contextual investigations: True Uses of MRP and ERP
MRP in Assembling Proficiency: Assembling Organization
- Assembling organization, a fair-sized auto parts maker, executed MRP to smooth its creation processes.
- Confronting difficulties in stock control and creation delays, the organization utilized MRP to streamline Manufacturing preparation and creation booking.
- The framework kept up with ideal stock levels, lessening conveying costs and guaranteeing convenient parts conveyance.
ERP Combination in a Worldwide Store Network: GlobalTech Arrangements
- GlobalTech Arrangements, a worldwide hardware partnership, embraced ERP to address the intricacies of its worldwide inventory network.
- With tasks spreading over different nations, GlobalTech confronted difficulties organizing additional capabilities, from acquirement to dissemination. ERP’s coordinated modules, including Store network The executives and money, gave a brought together stage.
- GlobalTech saw a remarkable improvement in functional effectiveness, cost administration, and responsiveness to showcase elements.
ERP in Help Arranged Organizations: ServicePro Counseling Firm
- ServicePro, a counseling firm contributing a scope of expert administrations, executed ERP to oversee different client projects effectively. Preceding the ERP mix, the firm battled with divided data across offices, preventing cooperation.
- ERP’s Enterprise the board and CRM modules brought together client information, project timetables, and Resource designation.
- ServicePro encountered a positive effect on both inward tasks and client fulfillment.
For these situation studies, MRP and ERP frameworks exhibited their viability in tending to explicit difficulties, prompting work on productivity across assembling, worldwide stock chains, and administration-arranged organizations.
These genuine applications feature these frameworks’ versatility and groundbreaking capability in assorted business situations. Hence, this answers the question, “What is the difference between MRP and ERP software?”
See Also: Top Hospitality Software Solutions For Business Owners
FAQS
What is the primary focus of MRP software?
Manufacturing Requirements Planning (MRP) software primarily focuses on optimizing manufacturing processes, emphasizing efficient inventory management and scheduling to meet specific production needs.
How does ERP differ from MRP regarding scope?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) has a broader scope, encompassing various business functions beyond manufacturing, including finance, CRM, and supply chain management, offering a more comprehensive solution.
What factors should be considered by businesses when choosing between MRP and ERP?
Businesses should take into account their size, scale of operations, specific industry requirements and budget constraints. MRP suits smaller, straightforward manufacturing, while ERP caters to larger, multifaceted enterprises with diverse needs.
Are there significant cost differences between MRP and ERP implementation?
Yes, MRP systems generally have lower upfront costs, making them budget-friendly for smaller businesses. In contrast, ERP implementation involves a higher initial investment due to its comprehensive functionalities and broader application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, grasping the distinctions between Manufacturing Requirements Planning (MRP) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is vital for businesses navigating operational decisions.
Moreover, tailoring choices based on size, industry, and specific needs ensures optimal utilization of these systems, laying the groundwork for enhanced efficiency and sustainable growth.
See Also: 4 Best Business Coaching Models You Should Know About