Have you ever been puzzled over what distinguishes CMR vs. SMR drives? It’s critical to apprehend how these two technologies fluctuate due to the growing need for an information garage.
Hard drives using CMR store data on separate tracks, whereas those using SMR store data on overlapping routes. Regarding data transfer and retrieval times, CMR hard drives are speedier than SMR.
In this text, we will observe the primary variations between CMR vs. SMR drives, at the side of their respective pros and cons, and determine which of the two kinds is the right choice for your desires. So, let us dive in and grab more excellent information about both of them and their differences.
Table of Contents
What is CMR?
CMR, called PMR (Perpendicular Magnetic Recording), is the conventional approach to storing facts on a hard drive. In a CMR hard drive, you can store information on individual tracks perpendicular to the disk’s surface. A little space called the “track pitch” separates the ways.
One of the main benefits of CMR technology is its ability to increase information density. This storage method can store more data on a surface area than other methods. That is because the tracks are densely packed, and the records are written perpendicularly, which permits a higher garage ability.
Calculating the storage capacity of a CMR pressure heavily relies on its areal density. This refers to the amount of data stored on a specific surface area. The tuning pitch determines the areal density, the range of tracks in step with inch (TPI), and the bits in step with inch (BPI). Because the areal density increases, the garage capability of the drive increases.
One of the challenges in growing the areal density of CMR drives is the superparamagnetic restriction, which is the factor at which the magnetic domains at the media turn out to be so small that they become unstable and prone to loss of statistics. 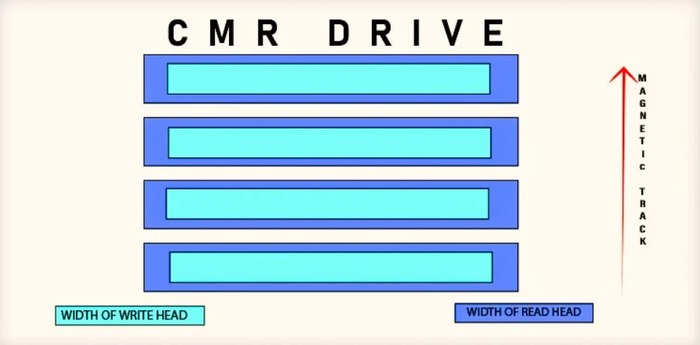
Manufacturers have used numerous strategies to overcome this restriction, including perpendicular magnetic recording, warmth-assisted Magnetic Recording (HAMR), and microwave-assisted magnetic recording (MAMR).
HAMR and MAMR are strategies of using warmth or microwaves to the media to make it more receptive to magnetic changes, which also lets in for better areal density. Perpendicular magnetic recording is a method of writing facts perpendicularly, permitting better areal density.
See Also: How Much Hard Drive Do I Need? | Types Of HDD
What is SMR?
Using SMR (Shingled Magnetic Recording) technology, hard disk drives (HDDs) can store data with increased storage capacity. To boost data density, the magnetic tracks are partially overlapped, or “shingled,” in an SMR hard drive. In the 1980s, the shingled magnetic recording was initially put out. Nevertheless, it recently gained popularity when it became practical, thanks to advancements in magnetic media and recording heads. The tracks’ overlap allows for storing more information in a given surface area. High-capacity drives, such as those used in servers or data centers, can particularly benefit from this.
In the 1980s, the shingled magnetic recording was initially put out. Nevertheless, it recently gained popularity when it became practical, thanks to advancements in magnetic media and recording heads. The tracks’ overlap allows for storing more information in a given surface area. High-capacity drives, such as those used in servers or data centers, can particularly benefit from this.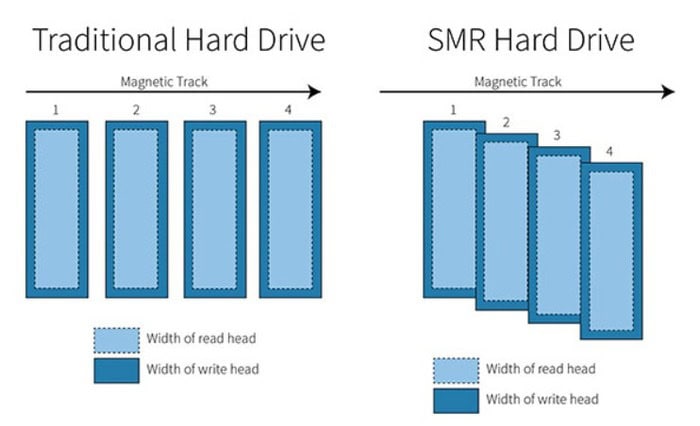 The tracks’ overlap, nevertheless, also has some negative aspects. The writing performance of SMR is one of its key drawbacks. Writing new data to the disk is more challenging since the tracks overlap partially. This is necessary to prevent the write head from disrupting the data on the overlapping routes. SMR drives, in comparison to conventional magnetic recording (CMR), have slower write rates.
The tracks’ overlap, nevertheless, also has some negative aspects. The writing performance of SMR is one of its key drawbacks. Writing new data to the disk is more challenging since the tracks overlap partially. This is necessary to prevent the write head from disrupting the data on the overlapping routes. SMR drives, in comparison to conventional magnetic recording (CMR), have slower write rates.
See Also: 13 Best Affordable Online File Hosting Services | Updated
Differences Between SMR VS CMR
Performance is one of the main distinctions between SMR vs. CMR. CMR drives improve data access efficiency by organizing it into separate tracks, leading to faster reading and writing.
SMR drives, on the other hand, have slower write rates as the write head needs to be more accurate to prevent disturbing the data on overlapping tracks. For programs like video editing or games that demand high write performance, this can be a problem.

Capacity is another crucial distinction between CMR VS. SMR drives. A Disk stores the data Data by creating perpendicular tracks with a narrower pitch on its surface.
SMR drives, on the other hand, offer a larger capacity since more information can remain on a given surface area, and the tracks overlap. SMR drives are better suited for high-capacity applications like those in servers or data centers.

The use of SMR drives has certain disadvantages as well. Because of the tracks’ overlap, which can lead to data loss over time, they might have a shorter lifespan than CMR drives and slower write rates.
Moreover, the tracks’ overlap makes accessing and modifying data more challenging, resulting in higher power usage and worse dependability. These were the fundamental differences between CMR vs. SMR drives.
See Also: Surface Pro 3 Won’t Turn On? Here’s How To Fix It
FAQS
Are SMR drives efficient to store data?
If you only sometimes need to retrieve the data, SMR drives are a good option for storage. They are a fantastic option for data preservation because of the capacity and dependency they offer. (For example, you might not want to keep a running copy of a software you often use on an SMR disk.)
Is the SMR disk suitable for RAID use?
SMR disks are RAID-compatible. However, there could be better options available. Just make sure the same technology powers both your devices. Choose a driving strategy and stay with it no matter what.
Drives: CMR vs. SMR; which should I pick?
Before picking up any of the two drives, ensure that you are aware of the storage and backup requirements behind your purpose. SMR drives should be able to offer the same amount of storage as CMR gadgets for less money per disk but with less usability.
What's CMR drive like?
As CMR drives provide a lot of advantages over conventional hard drives, they are growing in popularity. On CMR drives, data transmission speeds are greater and more reliable. CMR drives demand comparatively less power requirements. Portable devices, such as laptops, are well-suited for using these.
Conclusion
In contrast to CMR vs. SMR drives, CMR (Conventional Magnetic Recording) and SMR (Shingled Magnetic Recording) are two technologies used in hard disk drives (HDDs) to store data. CMR is the traditional method of storing data on HDDs, while SMR is a new hard drive technology designed to increase the storage capacity of the drives.
Overall, CMR vs. SMR drives have their strengths and weaknesses. CMR drives have good performance and are suitable for many applications but have lower storage capacity. SMR drives have higher storage capacity but may have slower write speeds and potentially lower lifespan. When selecting a dream, it is essential to consider the performance, power, and cost trade-offs.


