Unlocking the mysteries of your computer’s Central Processing Unit (CPU) involves understanding the enigmatic world of CPU pins. These tiny connectors, often overlooked, hold crucial significance in the seamless operation of your computer. They act as the communication bridge between the CPU and the motherboard. Let us know more about how many pins are on a CPU.
So, how many pins does a CPU have? The number of pins varies, but they commonly range from around 300 to 2000, depending on CPU model and generation. These pins serve as the physical interface. They facilitate data transmission between the CPU and other components and orchestrate the intricate dance of computing. You can learn to plug in case fans on Motherboard.
Why should you care about the number of pins on a CPU? Exploring this topic unveils the inner workings of your computer. Thus empowering you to make informed decisions when upgrading or building a system. Understanding the role of CPU pins enhances your overall comprehension of your computer’s functionality, making you a more confident user. Delve into the world of CPU pins, unravel the complexities, and grasp the essential knowledge to demystify your computer’s brain. Let us read more about how many pins are on a CPU.
Table of Contents
What Are CPU Pins?
CPU pins are small, metallic connectors. They form a critical link between the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and the motherboard in a computer system. These tiny connectors, often numbering in the hundreds to thousands, are integral to the seamless functioning of the entire system. Knowing your CPU model has several benefits, so you can learn to identify the CPU physically.
- These pins are the physical interface through which data and instructions travel between the CPU and the motherboard. The pins, acting like a communication bridge, play a crucial role in easing the exchange of information. They enable the CPU to coordinate the various tasks necessary for the computer to operate.
- The number of CPU pins can vary significantly across different CPU models and generations. While older CPUs may have fewer pins, modern processors can have over a thousand. This variation in pin count is influenced by factors such as the complexity of the processor, advancements in technology, and the specific requirements of the CPU model.
- Understanding the significance of CPU pins provides a greater insight into the intricacies of computer structure. The connectors ensure that the CPU can communicate efficiently with the motherboard, allowing for the rapid transmission of data and instructions.
- As technology advances, CPUs with more pins often indicate increased processing power and capabilities. It makes the exploration of CPU pins an essential aspect of comprehending the inner workings of a computer system.
Why Do CPUs Have Pins?
Before knowing “how many pins are on a cpu,” let’s explore why do CPUs have Pins. Pins on a CPU are fundamental to a computer system’s multifaceted functionality and performance. These small, metallic connectors serve many critical roles, each contributing to the seamless operation of the CPU. There are various online software to test CPU stress for free.
- CPU pins are essential for electrical connection. They establish the necessary pathways for electrical signals to flow between the CPU and its motherboard, facilitating data transmission of instructions vital for computing processes.
- The physical interface provided by CPU pins is crucial. It ensures a safe and stable connection between the CPU and its motherboard, allowing for reliable communication. This physical link is pivotal in maintaining the integrity of the data transfer process.

- The presence of pins facilitates easy replacement. Should a CPU become faulty or require an upgrade, the design with pins allows for straightforward removal and replacement, minimizing downtime and simplifying system maintenance.
- Thermal management is another critical function of CPU pins. The efficient dissipation of heat generated during processing is essential for preventing overheating. The design of CPU pins aids in the effective transfer of heat away from the processor, contributing to the overall thermal stability of the system.
- CPU pins play a significant role in supporting CPU design. The arrangement and number of pins are carefully engineered to accommodate the specific requirements and capabilities of the processor, allowing for optimal performance and reliability.
Therefore, including pins on a CPU is not a mere design choice but a strategic necessity. The intricate interplay of these connectors ensures the CPU’s smooth functioning, longevity, and adaptability within the computer system’s broader context. You can monitor CPU Temperature using multiple software.
Counting the Pins: Variability in Numbers
Examining the evolution of CPU PINs provides a fascinating historical perspective on the technological advancements that have shaped computer processors.
- Users have a question: “Do intel CPUs have pins?”. Older CPUs, like the Intel Pentium 4, had comparatively fewer pins, often numbering in the low hundreds. It reflected the technology available then and the less complex nature of early computing needs.
- In contrast, modern processors, exemplified by the Intel Core i7 and AMD Ryzen series, showcase a remarkable increase in pin counts. The Intel Core i7, for instance, can have over a thousand pins, indicating a significant leap in processing power and capabilities.
- This augmentation in PINs aligns with the ever-growing demands of contemporary computing, where complex tasks, multimedia processing, and resource-intensive applications are the norm.

- The variability in pin counts also stems from advancements in manufacturing processes. As technology has progressed, manufacturers can densely pack more transistors and circuitry onto a CPU, necessitating more pins for intricate communication between components. This trend showcases the relentless pursuit of efficiency and performance in computing.
- Comparing pin counts between older and modern CPUs underscores the dynamic nature of processor development. While the Intel Pentium 4, with its fewer pins, was once at the forefront of technology, today’s CPUs demand a higher pin count to meet the demands of contemporary computing tasks.
- This evolution is not just a numerical shift. It signifies a broader progression toward more powerful and capable processors, enabling computers to handle complex operations more efficiently.
Counting CPU pins unveils a journey through the history of computing, reflecting the ever-changing landscape of technology and the relentless pursuit of innovation in the quest for more powerful and capable processors. Wonder where the CPU stores its computation? Click Here.
Factors Influencing the Number of CPU Pins
The number of pins on a CPU is intricately tied to several key factors that collectively determine the processor’s architecture and functionality :
- Processor Architecture: The fundamental design of the processor, known as its architecture, heavily influences the number of pins. Different architectures prioritize varying aspects of performance, affecting the overall complexity and, subsequently, the pin count.
- Fused Components: CPUs often combine multiple components, like graphics processors, memory controllers, and cache. Including these integrated elements impacts the overall functionality of the CPU and contributes to the variation in pin count.
- Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process is critical in determining the number of CPU pins. Technological advancements allow manufacturers to create smaller, more efficient components, potentially influencing pin count reduction without compromising performance.
- Signal Integrity: Maintaining the integrity of signals passing through the pins is paramount for reliable performance. Factors like signal clarity, noise reduction, and data transmission speed can influence the CPU’s design and arrangement of pins.
- Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility with existing hardware and industry standards is key in determining pin count. Manufacturers strive to balance innovation with compatibility, as changes in pin configuration may impact a processor’s compatibility with existing motherboards.
Understanding these influencing factors sheds light on the intricate decisions made by CPU designers. It also allows users to comprehend why certain CPUs may have more or fewer pins than others.
As technology advances, manufacturers continually refine these factors to enhance CPU performance, reduce power consumption, and improve overall efficiency.
Types of CPU Sockets and Pin Counts
Understanding the various types of CPU sockets and their corresponding pin counts is crucial in deciphering the compatibility and performance of a processor. It brings users to the question: what are two common types of CPU sockets?
Well, Two prominent players in the CPU market are Intel and AMD. They utilize different socket designs – Intel uses Land Grid Array (LGA), and AMD employs Pin Grid Array (PGA).
Intel Sockets
Intel’s LGA sockets, such as the widely used LGA1200 for 10th and 11th Gen processors, have pins on the motherboard rather than the CPU. The CPU socket pins align with the processor pads, ensuring a secure, reliable connection.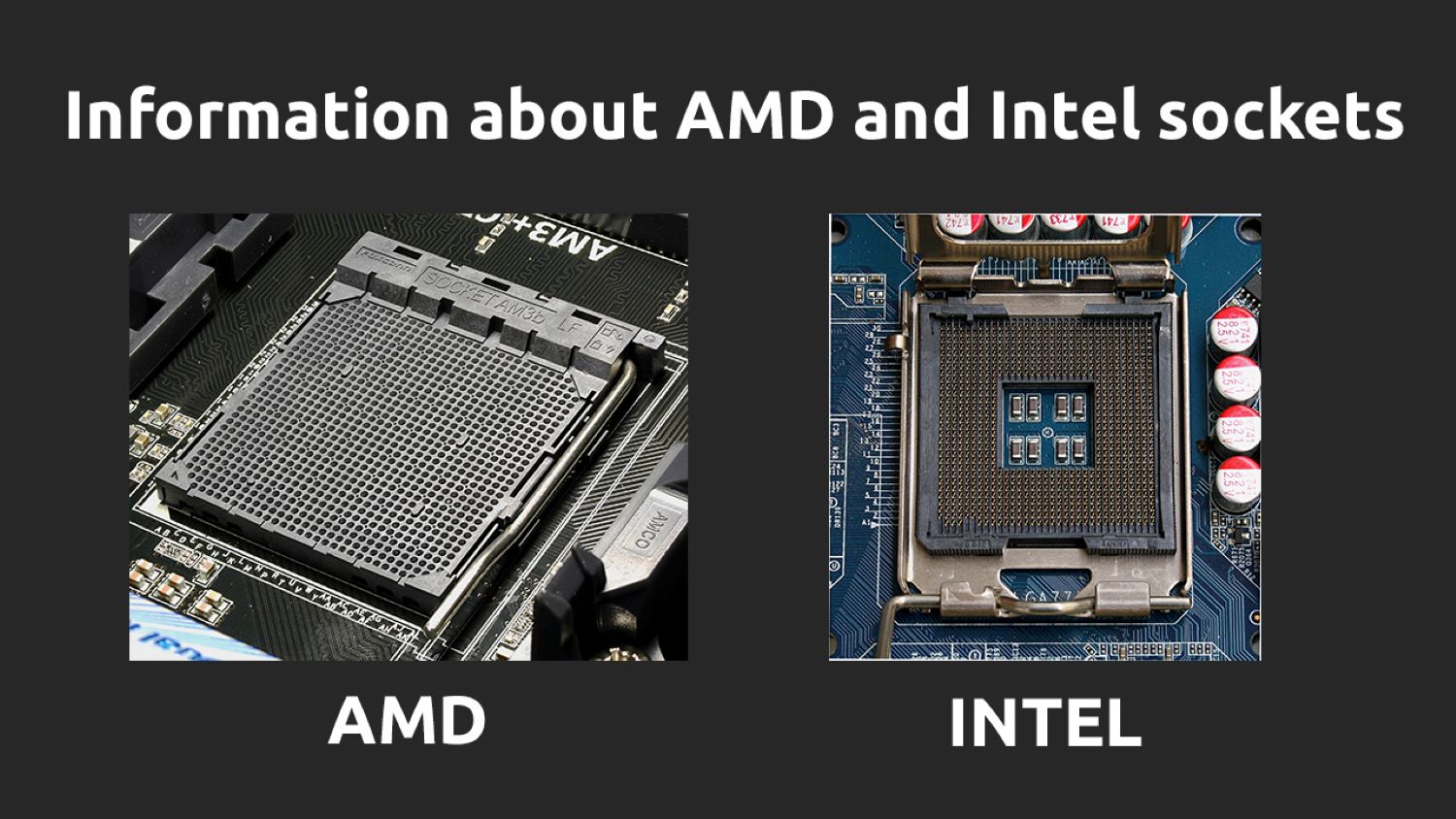
This design simplifies CPU installation and replacement, and LGA sockets often feature higher pin counts, contributing to enhanced connectivity and data transfer capabilities.
AMD Sockets
On the other hand, AMD utilizes PGA sockets, like the AM4 socket for Ryzen processors, where the pins are on the CPU. The PGA design simplifies the manufacturing process for CPUs but demands precision during installation to prevent damage to the delicate pins.
PGA sockets often have slightly lower pin counts than LGA sockets, but technological advancements have allowed AMD processors to deliver comparable performance.
The pin count in CPU sockets can vary significantly. For example, Intel’s LGA1200 has 1200 pins, while AMD’s AM4 socket typically has fewer.  Higher pin counts generally indicate a more advanced and feature-rich processor capable of handling complex computing tasks.
Higher pin counts generally indicate a more advanced and feature-rich processor capable of handling complex computing tasks.
However, it’s essential to note that a higher pin count doesn’t necessarily translate to better performance; it also depends on the processor’s architecture, design, and efficiency.
Choosing the proper CPU socket is critical when building or upgrading a system. Ensuring compatibility between the CPU and motherboard socket is essential for optimal performance.
Performance and Compatibility: The Impact of Pin Numbers
Now, how many are there? The next time you go to buy a CPU. It makes it vital for an individual to understand the impact of pins.
- The number of pins on a CPU isn’t merely a technical detail; it significantly influences the processor’s performance and compatibility with motherboards. Understanding this impact is crucial when navigating the world of computer hardware.
- A CPU in the count is fundamentally tied to its performance capabilities. Processors with a higher pin count often indicate advanced architectures and enhanced capabilities.
- More pins mean increased data transfer pathways, allowing faster communication between the CPU and other system components. Its heightened connectivity contributes to improved processing speeds and overall system performance.
- Moreover, the relationship between CPU pins and motherboard compatibility is critical.
 Motherboards are designed with specific socket types, and each socket corresponds to a particular CPU pin configuration.
Motherboards are designed with specific socket types, and each socket corresponds to a particular CPU pin configuration. - Ensuring compatibility is essential when upgrading or building a system. Placing a CPU with an incompatible pin count into a motherboard can lead to damage and system failure.
- Different generations of CPUs may introduce changes in pin count to accommodate technological advancements and performance requirements.
- Matching the CPU’s pin configuration with the corresponding socket on the motherboard is crucial. Manufacturers often provide detailed specifications to guide users in selecting compatible components.
While a higher pin count generally signifies a more powerful CPU, it’s essential to strike a balance based on your computing needs.
A mid-range processor with a moderate pin count may suffice for everyday tasks, offering a cost-effective solution without sacrificing performance.
On the other hand, enthusiasts or professionals engaged in resource-intensive activities may opt for CPUs with a higher pin count to meet their demanding requirements. Let us see more on how many pins are there.
Recent Developments in CPU Pin Technology
In the ever-evolving landscape of computer technology, recent years have witnessed significant advancements in CPU pin designs, revolutionizing how processors connect and communicate within computer systems.
One notable development is the exploration of pinless designs. Traditionally, CPU pins were the physical connectors that established contact with the motherboard.
However, recent innovations have seen pinless CPUs emerge, where a contact array or pad replaces direct physical pins. This breakthrough smoothens the manufacturing processes and enhances a CPU’s overall durability and reliability.
Another noteworthy trend is the pursuit of increased pin density. With the demand for higher processing power, CPU manufacturers are packing more pins into smaller spaces.
This higher pin density allows more efficient communication between the CPU and the motherboard, enhancing data transfer rates and overall system performance.
Enhanced signal integrity is another key focus in recent CPU pin technology developments. As CPUs become more powerful, the demand for faster data transfer increases. Thus, maintaining the integrity of signals transmitted through the pins becomes critical.
Manufacturers are implementing advanced technologies to minimize signal loss and interference, ensuring data travels accurately and swiftly between the CPU and other components.
These developments signify a shift in the physical structure of CPU pins and underscore the industry’s commitment to improving overall system performance.
Pinless designs, increased pin density, and enhanced signal integrity collectively contribute to more robust and efficient CPU architectures.
As consumers demand faster and more powerful computing experiences, these advancements in CPU pin technology play a pivotal role in meeting these expectations and shaping the future of computer processing. So, that is all about how many pins are on a CPU.
FAQs
Why do CPU pins bend so easily? Are they fragile?
CPU pins can bend pretty easily since they're tiny and poking out, but they're not actually that fragile. They're made from durable metal; they need more structural support. As long as you're gentle when handling processors and plugging them in, bent pins aren't usually an issue.
Should I bend the pins back into place myself?
It's recommended if you know what you're doing. CPU pins are very small, and it's easy to damage them further if you're not careful accidentally. A professional can repair slightly bent pins, but beyond that, it's usually safer and cheaper to replace the CPU. Prevention is key - be gentle whenever handling processors.
Is there a standard pin layout across CPUs?
While the overall function is the same, the physical pin layout does vary between CPU sockets and generations. Different sockets support features requiring more or fewer pins in certain positions. However, pins within the same socket type (like LGA1200) maintain a consistent layout.
What if a pin is missing? Will the CPU still work?
In most cases, the CPU will likely only function if even one pin is present. Modern CPUs rely on splitting different signals across multiple pins to operate properly. While a single bent pin might not kill it, a missing pin eliminates an essential connection.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of computer technology, comprehending the intricacies of CPU pins becomes paramount.
The exploration of advancements, including pin-less designs, increased pin density, and enhanced signal integrity, underscores the dynamic nature of CPU pin technology.
It satisfies your curiosity about CPU pins and their work! While the inner workings of computers can seem complex, trying to learn about components like this helps make it more relatable. If your computer shuts down while gaming, you can fix your PSU.
Feel free to reach out if any other questions arise – we enjoy sharing what we know about tech. Happy computing with this article on how many pins are on a CPU.
