Have you given any thought to how long does a CPU last? Do you want to learn more about the average lifespan of humans and the factors that affect it? Learn everything there is to know regarding CPU lifespan by reading up on it.
Although a CPU’s lifespan may differ, one should plan on using and caring for one for at least five to 10 years. Operational conditions and technological improvements may impact its lifetime. Read on to learn more about how long does a CPU last and whether your CPU is dying.
Understanding CPU lifespan is crucial for optimizing computer performance and cost efficiency. Factors such as thermal management, voltage stability, workload intensity, and manufacturing quality significantly impact the longevity of a CPU. Awareness of these factors helps users make informed decisions about maintenance and upgrade. Let us read on to know more.
Table of Contents
Why is a CPU’s Lifespan Important, and What Is a CPU?
The central part of a computer system responsible for performing calculations and issuing commands is the central processing unit. It is usually known as the “brain” of the computer. The CPU comprises several components, including the control unit, arithmetic logic unit, and cache memory. 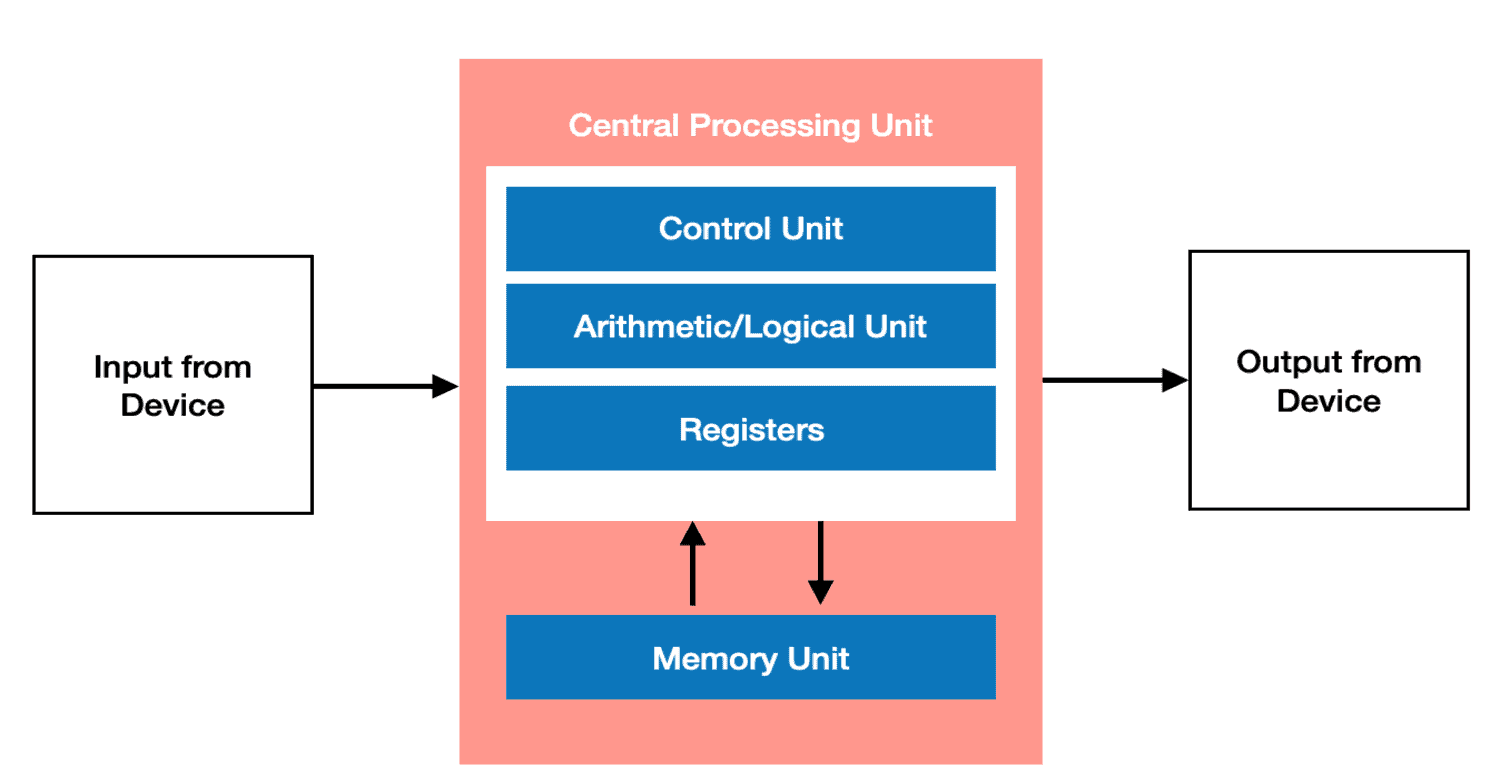
Due to the CPU’s crucial function in computer performance, its longevity is of utmost significance. The CPU manages the system’s processing requirements as the principal processor—a functional CPU guarantees smooth operation and effective software program execution.
The performance of a computer’s CPU has a significant impact on its speed and responsiveness. A powerful and quick CPU enables quicker data processing, multitasking abilities, and enhanced user experiences. The need for regular upgrades or replacements is also diminished by a longer CPU lifespan, which can result in cost savings. Now, let us read more to know how long a CPU lasts. You can know more about the CPU package by clicking on this link.
See Also: How to Fix YouTube Black Screen on Google Chrome Easily
Factors that Influence the Lifespan of a CPU
Several factors, including manufacturing quality and defects, operating temperatures, voltage levels, and usage patterns, can impact a CPU’s longevity. Let’s look more closely at each of these components:
Manufacturing Quality and Defects
The manufacturing process dramatically influences its lifespan. The CPU is designed to endure pressure and perform dependably over an extended period, thanks to high-quality manufacture. Conversely, production flaws may cause a product to fail sooner or have a shorter lifespan. The performance and durability of the CPU might be affected by deficiencies like flawed circuitry, shoddy soldering, or insufficient quality control.
Operating Temperatures
A CPU’s lifespan is significantly influenced by the temperature at which it runs. The heat produced by CPU activity might eventually cause the components to deteriorate. To avoid overheating, ideal temperature levels must be maintained. Check out this article to know more about safe CPU temperature.
To disperse heat properly and keep the CPU within acceptable operating temperatures, adequate cooling solutions are required, such as heat sinks, fans, or liquid cooling systems.
Voltage Levels
Another vital factor is the voltage sent to the CPU. Voltage fluctuations can cause the CPU to fail early, affecting its stability and dependability. Ensuring it receives a steady and continuous power supply within the manufacturer’s recommended voltage range is essential. The lifespan of the processor might be shortened by power spikes or insufficient voltage management. So, when thinking about “how long does the CPU last so early,” this could be a possible reason.
Usage Patterns
A CPU’s lifetime can also be affected by how it is utilized. The amount of stress on the CPU depends on the workload volume and use habits. CPUs may suffer more wear and tear than those with lesser workloads if they undertake more computationally intensive activities or operate at high clock speeds for extended periods. The CPU might experience more stress and could have a shorter lifespan due to factors like overclocking, using resource-demanding apps, or operating it at maximum capacity for lengthy periods. You can make your CPU work faster by understanding about CPU pins as it acts as a communication bridge with the motherboard, but to do this, you must know how many pins are on a CPU that you are using.
See Also: 4 Best Free VPN for Chrome to Ensure Complete Safety
Average Lifespan of a CPU
A CPU typically lasts between 5 and 10 years on average. It is crucial to remember that this estimate might change based on several variables, including the CPU’s performance, use trends, and technical improvements. So this is how long will a CPU last.
Consumer-grade CPUs, commonly used in personal computers, have a lifespan towards the lower end of this range. This is because consumer CPUs are often subject to moderate workloads and may need to be designed to withstand heavy usage over extended periods. 
In contrast, enterprise-grade CPUs, designed for servers and high-performance computing environments, are designed to handle more intensive workloads and are engineered for more excellent durability. These CPUs often have a longer average lifespan compared to consumer-grade counterparts.
Technological advancements and evolving computing needs may prompt users to upgrade their processors before the end of their lifespan. Factors such as the need for improved performance, compatibility with new software, or energy efficiency considerations can influence the decision to replace a CPU even if it is still functioning within its expected lifespan. Now you must know how long do processors last.
See Also: 14 Best Free CAD Software For Windows – TechWhoop
Signs Your CPU is Dying
Several signs indicate your CPU may be reaching the end of its lifespan. Being aware of these signs can help you diagnose and address potential issues. Here are some common signs : 
Unexpected Shutdowns or Restarts
If your computer frequently shuts down or restarts without apparent reason, it could be a sign of CPU problems. As a CPU deteriorates, it may struggle to handle tasks and become unstable, leading to unexpected system shutdowns or reboots.
Frequent Blue Screen Errors
Blue screen errors, or the “Blue Screen of Death” (BSOD), can occur due to CPU-related issues. If you consistently experience blue screen errors with error codes or system crash dumps, it may indicate CPU problems.
Performance Degradation
A dying CPU may struggle to keep up with demanding tasks, resulting in noticeable performance degradation. You may experience sluggishness, delays in program execution, or overall system slowdowns, even with routine tasks.
Overheating Issues
CPUs generate heat during operation, and overheating can significantly impact their lifespan. Thermal throttling, rapid temperature increases, or frequent computer shutdowns due to overheating might all be signs of CPU-related issues. A computer user must know what is the dangerous temperature for a CPU, to prevent further damage.
It’s important to note that other hardware or software issues can also cause these signs. If you observe these symptoms, seeking professional assistance or performing troubleshooting steps is recommended to accurately identify the underlying cause and determine if the processor is the culprit.
See Also: Free Malware Removal Tool For Windows In 2024 [Top 10]
How to Extend the Life of Your
To extend your CPU’s life, you can follow several vital practices. First and foremost, ensure proper cooling solutions are in place to prevent overheating. This includes using efficient CPU coolers and providing adequate airflow within your system.
Regular cleaning is also crucial to avoid dust buildup, as accumulated dust can hinder cooling performance and increase temperatures. Regularly remove dust from your CPU heatsink and fans using compressed air or a soft brush.
Avoid overclocking your CPU or follow safe overclocking practices if necessary. Overclocking can increase the strain on your processor, leading to higher temperatures and reduced lifespan.
Lastly, use surge protectors to safeguard your processor from power fluctuations or electrical surges that can damage its components. A good surge protector can protect your CPU and other sensitive electronics long-term.
See Also: 13 Best Free Adware Removal Software | Updated
Replacing vs. Upgrading Your CPU
A number of variables determine when to update or replace your CPU. It could be time for a new one if your old one is outdated and no longer fulfills your performance requirements. This is especially true if your processor cannot run more recent software or is incompatible with hardware requirements.
A CPU upgrade, however, has several advantages. It can boost the processing capability of your system, improve multitasking, and improve system performance. If your motherboard is compatible with more recent CPU types and the performance boost justifies the price, upgrading can be a good idea. 
Speaking of prices, it’s crucial to consider them while choosing between updating and replacing. A new motherboard and other components must be purchased when a CPU needs to be replaced, which typically results in higher costs. However, upgrading can be more affordable as it requires buying a new one.
Ultimately, your demands, compatibility issues, and available cash should be considered when deciding whether to replace or update your CPU.
Modern CPUs and Their Expected Longevity
Technology advancements have significantly impacted the expected longevity of modern CPUs. With each new generation of CPUs, manufacturers strive to improve their products’ performance, efficiency, and durability. You can now also stress test your CPU to figure out its full capability.
One way technology advancements have influenced lifespan is by introducing smaller fabrication processes. Smaller transistors provide higher transistor densities and reduced power requirements, which extend lifetime by lowering heat production and boosting efficiency.
Furthermore, contemporary CPUs frequently have durability-enhancing technologies integrated right into them. These include extensive error-correcting capabilities to reduce data corruption and thermal protection systems to minimize overheating. Dynamic voltage and frequency scaling also help to optimize power usage.
Longer lifespans of CPUs are also a result of improvements in general dependability and quality control brought about by advances in manufacturing procedures. It’s crucial to remember that several variables, including operating circumstances, workload intensity, and adequate maintenance, can still impact a CPU’s lifetime. So this is all about how long do processors last.
See also: How to Remove Shortcut Virus from Pendrive / Computer
FAQs
Can a CPU die suddenly?
While rare, it can fail suddenly due to manufacturing defects, electrical surges, or extreme overheating. However, most CPU failures occur gradually over time due to wear and tear or improper usage.
Does overclocking reduce CPU lifespan?
Overclocking can reduce a CPU's lifespan due to increased heat generation and stress on the components. However, when done responsibly with appropriate cooling and within safe limits, the impact on longevity can be minimal.
Can a CPU be repaired if it fails?
They are not typically repairable, as their complex integrated circuits make it impractical to fix individual components. If a processor fails, it usually requires replacement with a new one.
Is it worth upgrading an old CPU, or is it better to replace it?
Your particular demands and financial situation will determine this. Upgrading to a newer model may be advantageous if your old processor can no longer handle your performance demands or is incompatible with more recent technology. However, affordability and compatibility issues need to be taken into mind.
Conclusion
Understanding the lifespan of your CPU is crucial for optimizing its performance and longevity. Regular maintenance, such as proper cooling, cleaning, and avoiding excessive overclocking, can help extend its lifespan. Stay informed about technological advancements and make informed choices to ensure your CPU serves you well for years. This article on how long does a CPU last has helped you know everything about it.


